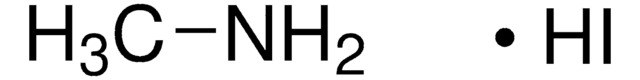Kluczowe dokumenty
806390
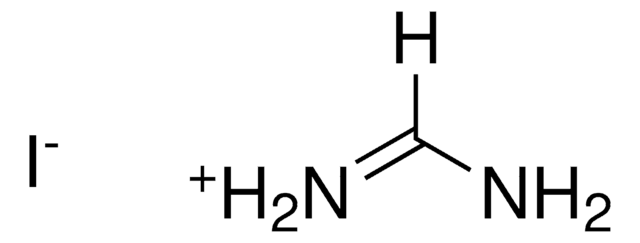
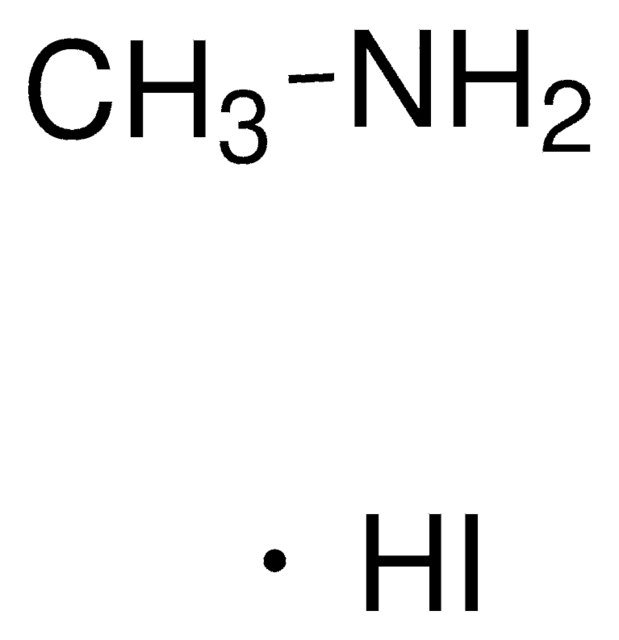
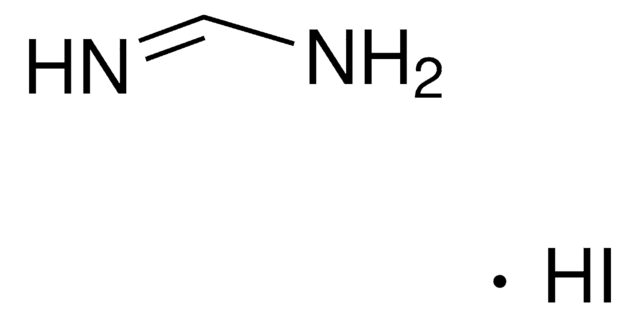
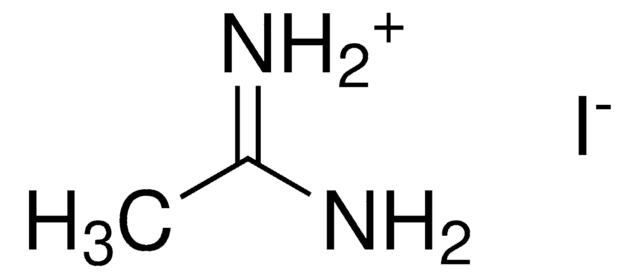
Methylammonium iodide
Synonim(y):
Methanamine hydriodide, Greatcell Solar®, Methanaminium iodide, Methylamine hydriodide, Methylamine hydroiodide, Monomethylammonium iodide
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Formularz
powder
Poziom jakości
charakterystyka ekologicznej alternatywy
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
mp
145 °C
kategoria ekologicznej alternatywy
, Enabling
ciąg SMILES
CN.I
InChI
1S/CH5N.HI/c1-2;/h2H2,1H3;1H
Klucz InChI
LLWRXQXPJMPHLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Informacje prawne
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Next generation solar cells have the potential to achieve conversion efficiencies beyond the Shockley-Queisser (S-Q) limit while also significantly lowering production costs.
Dr. Perini and Professor Correa-Baena discuss the latest research and effort to obtain higher performance and stability of perovskite materials.
Dr Perini i profesor Correa-Baena omawiają najnowsze badania i wysiłki zmierzające do uzyskania wyższej wydajności i stabilności materiałów perowskitowych.
For several decades, the need for an environmentally sustainable and commercially viable source of energy has driven extensive research aimed at achieving high efficiency power generation systems that can be manufactured at low cost.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej