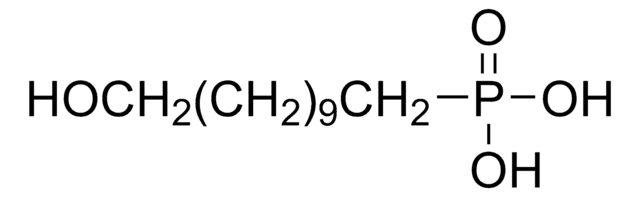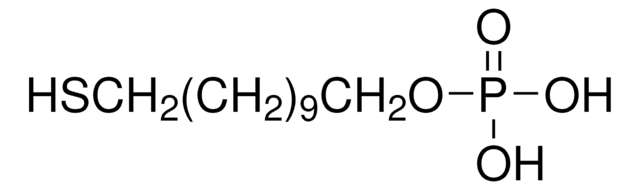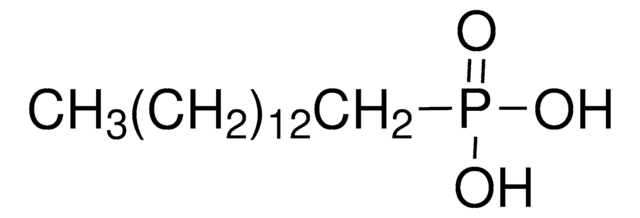Key Documents
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Próba
97%
Postać
solid
mp
129-133 °C
ciąg SMILES
OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCP(O)(O)=O
InChI
1S/C16H33O5P/c17-16(18)14-12-10-8-6-4-2-1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-22(19,20)21/h1-15H2,(H,17,18)(H2,19,20,21)
Klucz InChI
JVXYHUCXFLBBGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
There is widespread demand for thin, lightweight, and flexible electronic devices such as displays, sensors, actuators, and radio-frequency identification tags (RFIDs). Flexibility is necessary for scalability, portability, and mechanical robustness.
Inorganic nanomaterials are tunable by size, shape, structure, and/or composition. Advances in the synthesis of well-defined nanomaterials have enabled control over their unique optical, electronic, and chemical properties stimulating tremendous interest across a wide range of disciplines. This article illuminates some of the recent research advances of inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) in optoelectronics applications.
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) have attracted enormous interest for a wide variety of applications in micro- and nano-technology. In this article, we compare the benefits of three different classes of SAM systems (alkylthiolates on gold.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej