Key Documents
229601
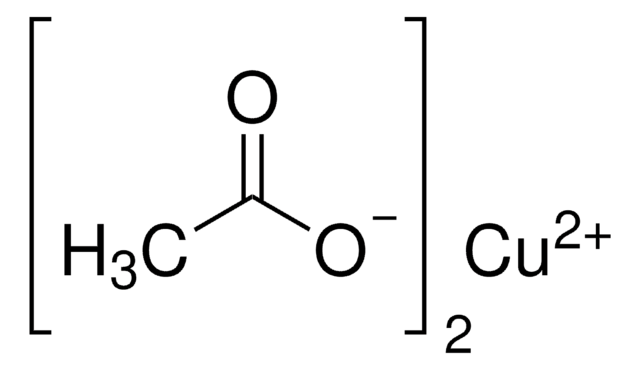
Copper(II) acetate monohydrate
99.99% trace metals basis
Synonim(y):
Cupric acetate monohydrate
About This Item
Polecane produkty
gęstość pary
6.8 (vs air)
Próba
99.99% trace metals basis
Postać
powder or crystals
przydatność reakcji
core: copper
charakterystyka ekologicznej alternatywy
Catalysis
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
kategoria ekologicznej alternatywy
ciąg SMILES
O.CC(=O)O[Cu]OC(C)=O
InChI
1S/2C2H4O2.Cu.H2O/c2*1-2(3)4;;/h2*1H3,(H,3,4);;1H2/q;;+2;/p-2
Klucz InChI
NWFNSTOSIVLCJA-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Kod klasy składowania
8B - Non-combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
does not flash
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
does not flash
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
In this article, we will discuss coinage metal deposition processes in order to provide a sense of the most critical precursors, reducing agents, and processes.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej