ABT1388
Anti-Phospho-Lamin A/C (Ser390)
from rabbit
別名:
Prelamin A/C, Renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-32
ログイン組織・契約価格を表示する
すべての画像(2)
About This Item
UNSPSCコード:
12352203
eCl@ss:
32160702
NACRES:
NA.41
クローン:
polyclonal
application:
WB
inhibition assay
inhibition assay
化学種の反応性:
human
テクニック:
inhibition assay: suitable (peptide)
western blot: suitable
western blot: suitable
citations:
1
おすすめの製品
由来生物
rabbit
抗体製品の状態
affinity isolated antibody
抗体製品タイプ
primary antibodies
クローン
polyclonal
化学種の反応性
human
テクニック
inhibition assay: suitable (peptide)
western blot: suitable
アイソタイプ
IgG
NCBIアクセッション番号
UniProtアクセッション番号
ターゲットの翻訳後修飾
phosphorylation (pSer390)
遺伝子情報
human ... LMNA(4000)
詳細
Prelamin-A/C (UniProt: P02545) is encoded by the LMNA (also known as LMN1) gene (Gene ID: 4000) in human. Prelamin-A/C is subsequently cleaved into Lamin A/C. Lamins are components of the nuclear lamina that provides a framework for the nuclear envelope and interact with chromatin. Prelamin-A/C
Is cleaved to generate Lamin A/C. Farnesylation of prelamin-A/C facilitates nuclear envelope targeting and subsequent cleavage by ZMPSTE24/FACE1 to remove the farnesyl group produces mature Lamin-A/C that is inserted into the nuclear lamina. Lamin A and C are present in equal amounts in the lamina of mammals and they play an important role in nuclear assembly, chromatin organization, nuclear membrane and telomere dynamics. Lamins are shown to be essential for normal development of peripheral nervous system and skeletal muscle and for muscle satellite cell proliferation. Lamins also prevent fat infiltration of muscle and bone marrow, helping to maintain the volume and strength of skeletal muscle and bone. Phosphorylation of Lamins is reported to occur continuously throughout all interphase periods and takes place mainly on the assembled lamina. Phosphorylation of the major polypeptides of the lamina induces laminar disassembly during mitosis. Phosphorylated Lamin-A/C localizes to nucleoplasm. Lamin A/C undergoes phosphorylation at multiple sites and one of the best characterized phosphorylation sites is on Serine 22 and it is phosphorylated during interphase. Phosphorylation of Serine 22 stabilizes Lamin A/C. Overexpression of Lamin-A is shown to result in greater phosphorylation of Serine 22 and 390 and Lamin A/C knockdowns display reduced phosphorylation at both sites, which helps in maintaining the integrity of the diminished lamina. Mutations in LMNA gene can cause Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 2 and 3, which are characterized by weakness and atrophy of muscle without involvement of the nervous system and cardiac conduction defects. Some mutations have also been linked to familial Lipodystrophy that leads to the loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue in the lower parts of the body and accumulation of adipose tissue in the face and neck. (Ref.: Buxboim, A., et al. (2014). Curr. Biol. 24(16): 1909-1917).
Is cleaved to generate Lamin A/C. Farnesylation of prelamin-A/C facilitates nuclear envelope targeting and subsequent cleavage by ZMPSTE24/FACE1 to remove the farnesyl group produces mature Lamin-A/C that is inserted into the nuclear lamina. Lamin A and C are present in equal amounts in the lamina of mammals and they play an important role in nuclear assembly, chromatin organization, nuclear membrane and telomere dynamics. Lamins are shown to be essential for normal development of peripheral nervous system and skeletal muscle and for muscle satellite cell proliferation. Lamins also prevent fat infiltration of muscle and bone marrow, helping to maintain the volume and strength of skeletal muscle and bone. Phosphorylation of Lamins is reported to occur continuously throughout all interphase periods and takes place mainly on the assembled lamina. Phosphorylation of the major polypeptides of the lamina induces laminar disassembly during mitosis. Phosphorylated Lamin-A/C localizes to nucleoplasm. Lamin A/C undergoes phosphorylation at multiple sites and one of the best characterized phosphorylation sites is on Serine 22 and it is phosphorylated during interphase. Phosphorylation of Serine 22 stabilizes Lamin A/C. Overexpression of Lamin-A is shown to result in greater phosphorylation of Serine 22 and 390 and Lamin A/C knockdowns display reduced phosphorylation at both sites, which helps in maintaining the integrity of the diminished lamina. Mutations in LMNA gene can cause Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 2 and 3, which are characterized by weakness and atrophy of muscle without involvement of the nervous system and cardiac conduction defects. Some mutations have also been linked to familial Lipodystrophy that leads to the loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue in the lower parts of the body and accumulation of adipose tissue in the face and neck. (Ref.: Buxboim, A., et al. (2014). Curr. Biol. 24(16): 1909-1917).
特異性
This rabbit polyclonal antibody detects human Lamin A/C phosphorylated on serine 390.
免疫原
KLH-conjugated linear peptide corresponding to 11 amino acids from human Lamin A/C surrounding phosphorylated Serine 390.
アプリケーション
Anti-Phospho-Lamin A/C (Ser390), Cat. No. ABT1388, is a rabbit polyclonal antibody that detects Lamin A/C phosphorylated on Serine 390 and has been tested for use in Western Blotting and Peptide Inhibition Assay.
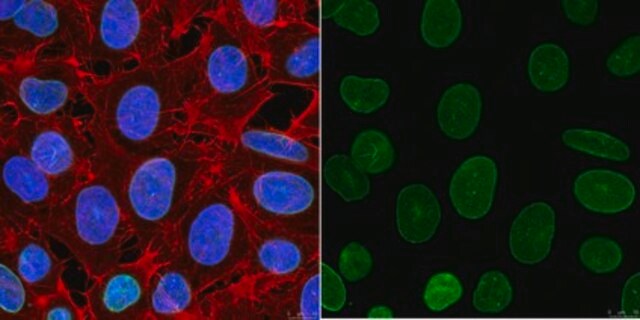
Peptide Inhibition Analysis: A 1:500 dilution from a representative lot was used with A549 cells (specific for Lamin A _C phosphorylation) for peptide block analysis.
品質
Evaluated by Western Blotting in A549 cells.
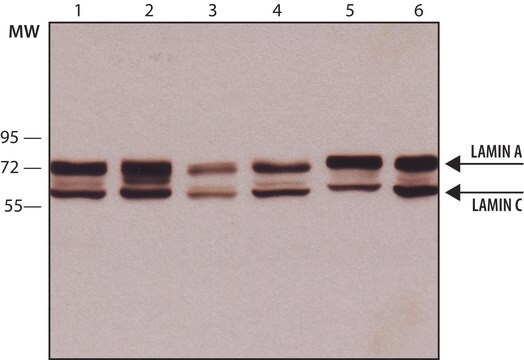
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:500 dilution of this antibody detected Phospho-Lamin A/C (Ser390) in A549 cells (specific for Lamin A/C phosphorylation).
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:500 dilution of this antibody detected Phospho-Lamin A/C (Ser390) in A549 cells (specific for Lamin A/C phosphorylation).
ターゲットの説明
~75 kDa and 65 kDa observed; 74.14 and 65.14 kDa calculated for Lamin A and C, respectively. Uncharacterized bands may be observed in some lysate(s).
物理的形状
Format: Purified
その他情報
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
適切な製品が見つかりませんか。
製品選択ツール.をお試しください
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)