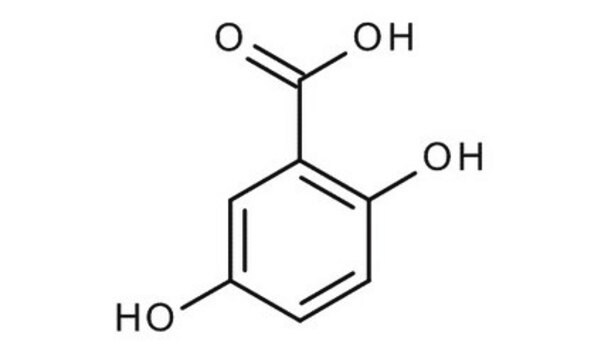
50862
Super-DHB
suitable for matrix substance for MALDI-MS, ≥99.0%
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥99.0% (sum of DHB and 2-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acid, HPLC)
≥99.0%
Classi funzionali degli analiti
polymers
Classi chimiche degli analiti
glycans, peptides, proteins
tecniche
MALDI-MS: suitable
Solubilità
methanol: 1%, clear
Cationi in tracce
Ca: ≤5 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤5 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Na: ≤5 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
Compatibilità
suitable for matrix substance for MALDI-MS
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- Glycan and Protein Analysis of Glycoengineered Bacterial E. coli Vaccines by MALDI-in-Source Decay FT-ICR Mass Spectrometry: This study demonstrates the application of Super-DHB as a matrix in advanced mass spectrometry for the detailed characterization of glycoengineered vaccines, essential for researchers in pharmaceuticals and life science manufacturing (Nicolardi et al., 2022).
- An Improved Method for Rapid Detection of Mycobacterium abscessus Complex Based on Species-Specific Lipid Fingerprint by Routine MALDI-TOF: Highlights the use of Super-DHB in enhancing the lipid fingerprinting capabilities of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, critical for rapid microbial identification in medical microbiology and pharmaceutical research (Jia Khor et al., 2021).
- Discrimination of bovine milk from non-dairy milk by lipids fingerprinting using routine matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry: Illustrates the role of Super-DHB in differentiating dairy and non-dairy milks based on lipid profiles using MALDI-MS, vital for food scientists and chemists in quality control and food safety (England et al., 2020).
Confezionamento
Risultati analitici
Prodotti correlati
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.

![trans-2-[3-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-2-methyl-2-propenylidene]malononitrile matrix substance for MALDI-MS, ≥99.0% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/249/587/f8021369-f65a-413d-887d-3c8a4d2a248f/640/f8021369-f65a-413d-887d-3c8a4d2a248f.png)