推荐产品
生物源
synthetic (organic)
品質等級
agency
USP/NF
meets USP testing specifications
化驗
97.0-102.0%
形狀
solid
mp
262-264 °C (lit.)
運輸包裝
ambient
儲存溫度
2-8°C
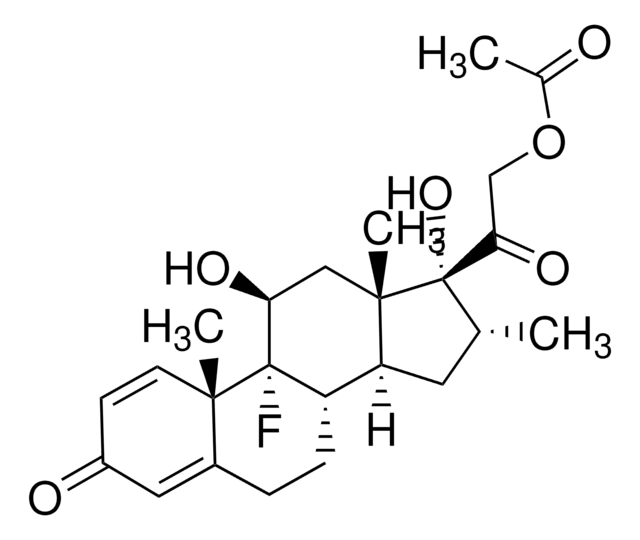
SMILES 字串
C[C@@H]1C[C@H]2[C@@H]3CCC4=CC(=O)C=C[C@]4(C)[C@@]3(F)[C@@H](O)C[C@]2(C)[C@@]1(O)C(=O)CO
InChI
1S/C22H29FO5/c1-12-8-16-15-5-4-13-9-14(25)6-7-19(13,2)21(15,23)17(26)10-20(16,3)22(12,28)18(27)11-24/h6-7,9,12,15-17,24,26,28H,4-5,8,10-11H2,1-3H3/t12-,15+,16+,17+,19+,20+,21+,22+/m1/s1
InChI 密鑰
UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N
基因資訊
human ... ABCB1(5243) , CYP3A4(1576) , IL4(3565) , IL5(3567) , NR3C1(2908)
mouse ... Abcb1a(18671) , Abcb1b(18669) , Ifng(15978) , Nos2(18126) , Ptgs2(19225) , Tnf(21926)
rat ... Ar(24208) , Nr3c1(24413) , Tnf(24835)
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
應用
- To investigate the osteogenic differentiation and chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
- In α-MEM (minimum essential medium) for inducing the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and umbilical cord blood.
- For the isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from 6- to 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice.
生化/生理作用
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Repr. 1B
儲存類別代碼
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
其他客户在看
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门