11119915001
Roche
RNase, DNase-free
from bovine pancreas
Sinónimos:
Rnase
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
bovine pancreas
Nivel de calidad
formulario
solution
actividad específica
≥30 units/mg protein
envase
pkg of 500 μg (1 ml)
fabricante / nombre comercial
Roche
técnicas
DNA purification: suitable
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Descripción general
Aplicación
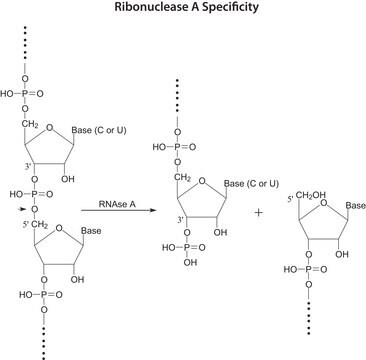
Definición de unidad
One unit produces a decrease in absorbance at 260 nm, which is equivalent to a total conversion of RNA to oligonucleotides in one minute at +25 °C.
Forma física
Nota de preparación
- For small-scale isolation of plasmid DNA ("miniprep" from a 1.5 ml bacterial culture), use 0.5 μl of RNase, DNase-free in a reaction volume of 50 μl.
- To isolate plasmid DNA from a 100 ml bacterial culture, use 8 μl of RNase, DNase-free in a reaction volume of 2 ml.
- To isolate genomic DNA from cultured mammalian cells (5 x 107 cells), use 8 μl of RNase, DNase-free in a reaction volume of 2 ml.
Working solution: Storage and Dilution Buffer: 10 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM CaCl2, 50% glycerol (v/v), pH 7.0.
Otras notas
Código de clase de almacenamiento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
No data available
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
No data available
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Protocolos
0.1 mU RNase, DNase-free degrades 1 μg RNA in 30 min at + 37 °C in a reaction volume of 50 μL PCR grade water. The protein concentration of RNase, DNase-free is 0.5 μg/μL.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico