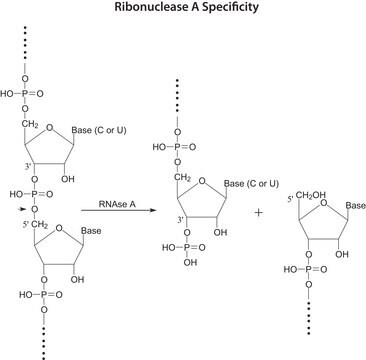
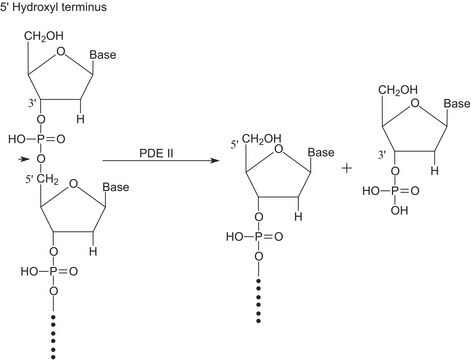
R1003
Ribonuclease T1 from Aspergillus oryzae
ammonium sulfate suspension, 300,000-600,000 units/mg protein
Sinónimos:
Guanyloribonuclease, Ribonucleate 3′-guanylo-oligonucleotidohydrolase
About This Item
origen biológico
Aspergillus sp. (Aspergillus oryzae)
Formulario
ammonium sulfate suspension
actividad específica
300,000-600,000 units/mg protein
mol peso
11068 by amino acid sequence
técnicas
cell based assay: suitable
idoneidad
suitable for separating native or denatured proteins, or nucleic acids
aplicaciones
cell analysis
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Aplicación
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Definición de unidad
Forma física
Nota de análisis
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Instructions for working with enzymes supplied as ammonium sulfate suspensions
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico