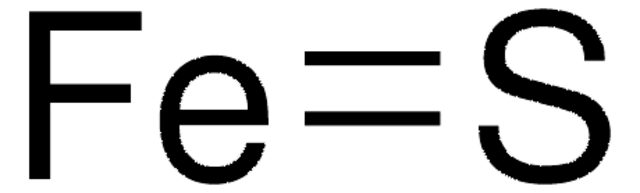343161
Iron(II) sulfide
−100 mesh, 99.9% trace metals basis
Sinonimo/i:
Ferrous sulfide
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula empirica (notazione di Hill):
FeS
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
87.91
Numero CE:
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
12352302
eCl@ss:
38190405
ID PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.55
Prodotti consigliati
Grado
for analytical purposes
Saggio
99.9% trace metals basis
Stato
powder
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
reagent type: catalyst
core: iron
Dimensione particelle
−100 mesh
Densità
4.84 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
S=[Fe]
InChI
1S/Fe.S
MBMLMWLHJBBADN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
- Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of microbial metal sulfide oxidation - part A: This study delves into the microbial oxidation of metal sulfides like Iron(II) sulfide, shedding light on bioleaching processes crucial for the extraction of valuable metals from ores, which is highly relevant for environmental and materials science applications (Vera et al., 2022).
- Novel QTL Associated with Aerenchyma-Mediated Radial Oxygen Loss (ROL) in Rice: Explores genetic traits influenced by conditions such as the presence of Iron(II) sulfide in paddy fields, providing insights into how rice adapts to iron-rich anaerobic soils, which is vital for agricultural biotechnology and crop science (Duyen et al., 2022).
- Fe(ii) and Fe(iii) dithiocarbamate complexes as single source precursors: Investigates the synthesis of nanoscale iron sulfides from these precursors, using in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy, which is essential for developing advanced materials with specific magnetic and electronic properties (Roffey et al., 2019).
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
The structural plasticity of the proximal [4Fe3S] cluster is responsible for the O2 tolerance of membrane-bound [NiFe] hydrogenases.
Jean-Marie Mouesca et al.
Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 52(7), 2002-2006 (2013-01-09)
David P Summers et al.
Astrobiology, 12(2), 107-114 (2012-01-31)
Understanding the abiotic fixation of nitrogen and how such fixation can be a supply of prebiotic nitrogen is critical for understanding both the planetary evolution of, and the potential origin of life on, terrestrial planets. As nitrogen is a biochemically
Mei Wang et al.
Dalton transactions (Cambridge, England : 2003), 40(48), 12793-12800 (2011-10-11)
The research on structural and functional biomimics of the active site of [FeFe]-hydrogenases is in an attempt to elucidate the mechanisms of H(2)-evolution and uptake at the [FeFe]-hydrogenase active site, and to learn from Nature how to create highly efficient
Vanessa N L Wong et al.
Water research, 47(2), 821-832 (2012-12-04)
Benthic sediments in coastal acid sulfate soil (CASS) drains can contain high concentrations (~1-5%) of acid volatile sulfide (AVS) as nano-particulate mackinawite. These sediments can sequester substantial quantities of trace metals. Because of their low elevation and the connectivity of
Thanh Binh Nguyen et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135(1), 118-121 (2012-12-20)
Iron sulfide generated in situ from elemental sulfur and iron was found to be highly efficient in catalyzing a redox/condensation cascade reaction between 2-amino/hydroxy nitrobenzenes and activated methyl groups. This method represents a straightforward and highly atom economical approach to
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.