400866
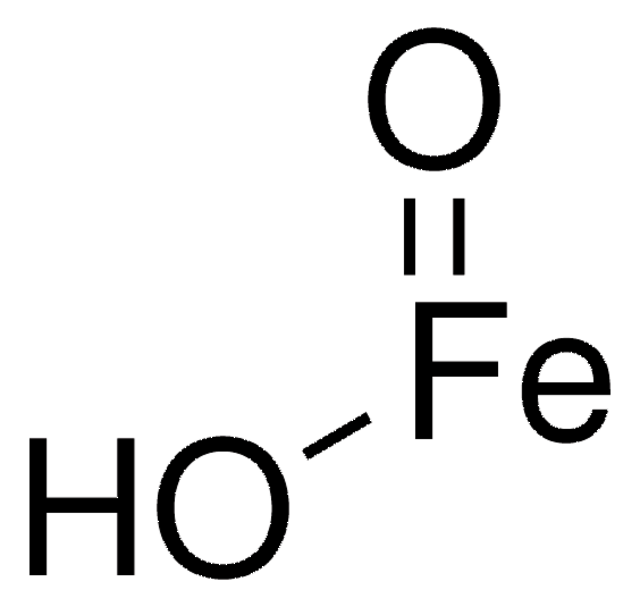
Iron(II) oxide
−10 mesh, ≥99.6% trace metals basis
Sinonimo/i:
Ferrous oxide, Iron monooxide
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥99.6% trace metals basis
Stato
powder
Impurezze
≤5% free iron
Dimensione particelle
−10 mesh
Densità
5.7 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
applicazioni
battery manufacturing
Stringa SMILE
O=[Fe]
InChI
1S/Fe.O
UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
nwg
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Magnetism and magnetic materials have been of scientific interest for over 1,000 years. More recently, fundamental investigations have focused on exploring the various types of magnetic materials and understanding the magnetic effects created by electric currents.
Magnetic materials permeate numerous daily activities in our lives. They are essential components of a diversity of products including hard drives that reliably store information on our computers, decorative magnets that keep the shopping list attached to the refrigerator door, electric bicycles that speed our commute to work, as well as wind turbines for conversion of wind energy to electrical power.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 400866-25G | 4061831985160 |
| 400866-5G | 4061831985177 |
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.