K0250
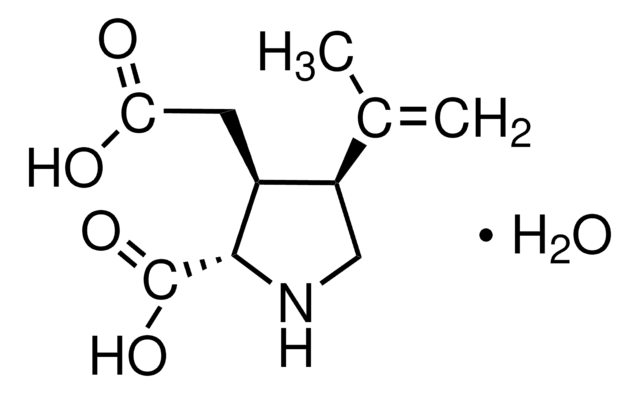
Kainic acid monohydrate
≥99% (TLC), powder, ionotropic glutamate receptor (kainate class) agonist
Sinônimo(s):
Digenin, Kainate, 2-Carboxy-3-carboxymethyl-4-isopropenylpyrrolidine
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nome do produto
Kainic acid monohydrate, ≥99% (TLC)
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥99% (TLC)
Formulário
powder
Impurezas
Glutamate, free
solubilidade
H2O: soluble
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O.CC(=C)[C@H]1CN[C@@H]([C@H]1CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H15NO4.H2O/c1-5(2)7-4-11-9(10(14)15)6(7)3-8(12)13;/h6-7,9,11H,1,3-4H2,2H3,(H,12,13)(H,14,15);1H2/t6-,7+,9-;/m0./s1
chave InChI
FZNZRJRSYLQHLT-SLGZUKMRSA-N
Informações sobre genes
human ... GRIA1(2890) , GRIA2(2891) , GRIA4(2893) , GRIK1(2897) , GRIK2(2898) , GRIK3(2899) , GRIK4(2900) , GRIK5(2901) , SLC1A1(6505) , SLC1A2(6506) , SLC1A3(6507)
mouse ... Gria1(14799)
rat ... Gria1(50592) , Grik1(29559) , Grik4(24406) , Grin2a(24409)
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- tostudy mechanisms of excitation-induced apoptosis and epilepsy.
- to hamper themitochondrial function ()
- used to induce c-fosexpression in the mice′s brains, specifically targeting the dorsal hippocampus.()
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Características e benefícios
Nota de preparo
produto relacionado
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Conteúdo relacionado
DISCOVER Bioactive Small Molecules for Neuroscience
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica