H8916
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α human
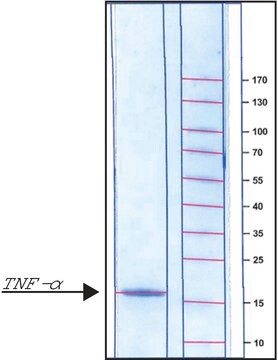
≥95% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in HEK 293 cells, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture
Sinônimo(s):
TNF-α
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nome do produto
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α human, Xeno-free, recombinant, expressed in HEK 293 cells, suitable for cell culture
fonte biológica
human
Nível de qualidade
recombinante
expressed in HEK 293 cells
Ensaio
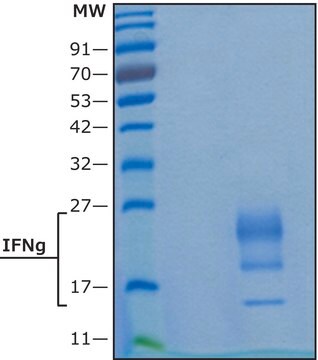
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
Formulário
lyophilized powder
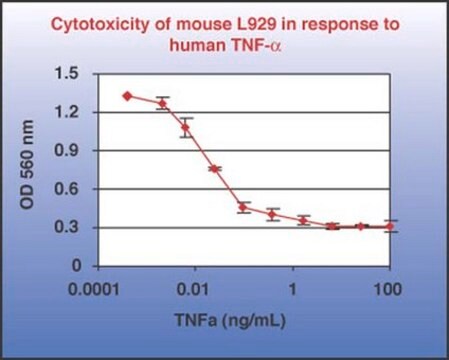
potência
≤1.0 ng/mL ED50
qualidade
endotoxin tested
peso molecular
17 kDa (glycosylated)
~17.4 kDa
embalagem
pkg of 10 μg
condição de armazenamento
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
técnica(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Impurezas
≤1.00 EU/μg (endotoxin)
nº de adesão UniProt
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
Informações sobre genes
human ... TNF(7124)
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
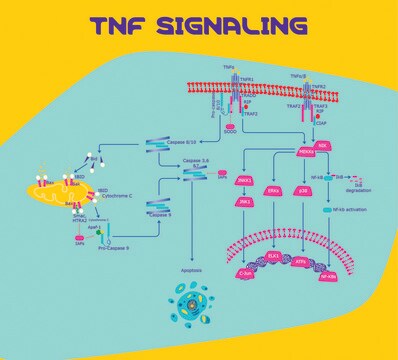
Descrição geral
Aplicação
- In induction of netting neutrophils by anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody and to study its effect on platelet activation and formation of monomeric C-reactive protein.
- To study the effect of TNF-α on miR-221 and fractalkine expression.
- To induce inflammatory cell responses.
- In NF-κB luciferase reporter assay.
- as a permeability inducing agent for endothelial cell monolayer permeability assay
- as a reactive oxygen species inducer in primary rat cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (RCMVECs)
- in the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293), neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells and HeLa cells
- in the stimulation of the human keratinocyte cell line(HaCaT) and human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs)
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Nota de preparo
Nota de análise
produto comparável
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 2
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
2 Replication of Classical Swine Fever Virus
Artigos
Lipid Induced Insulin Resistance
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica