A7469
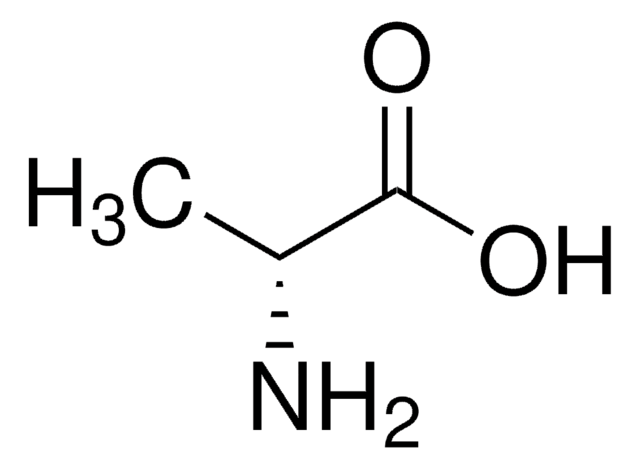
L-Alanine
98.5-101.0%, suitable for cell culture, BioXtra, non-animal source
Sinônimo(s):
(S)-2-Aminopropionic acid, L-α-Aminopropionic acid
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
product name
L-Alanine, from non-animal source, meets EP, USP testing specifications, suitable for cell culture, 98.5-101.0%
fonte biológica
non-animal source
Nível de qualidade
Agency
meets EP testing specifications
meets USP testing specifications
linha de produto
BioXtra
Ensaio
98.5-101.0%
forma
powder
técnica(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Impurezas
endotoxin, tested
cor
white
solubilidade
H2O: 100 mg/mL
aplicação(ões)
peptide synthesis
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
C[C@H](N)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C3H7NO2/c1-2(4)3(5)6/h2H,4H2,1H3,(H,5,6)/t2-/m0/s1
chave InChI
QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Aplicação
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Aplicação
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Equipamento de proteção individual
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Muscle
Artigos
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about how proliferatively active cells require both a source of carbon and of nitrogen for the synthesis of macromolecules. Although a large proportion of tumor cells utilize aerobic glycolysis and shunt metabolites away from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, many tumor cells exhibit increased mitochondrial activity.
Chromatograms
application for HPLCNossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica