67309
Kovac′s reagent for indoles
suitable for microbiology
Sinônimo(s):
4-(Dimethylamino)benzaldehyde solution
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Agency
according to ISO 16654:2001
Nível de qualidade
linha de produto
BioChemika
prazo de validade
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
composição
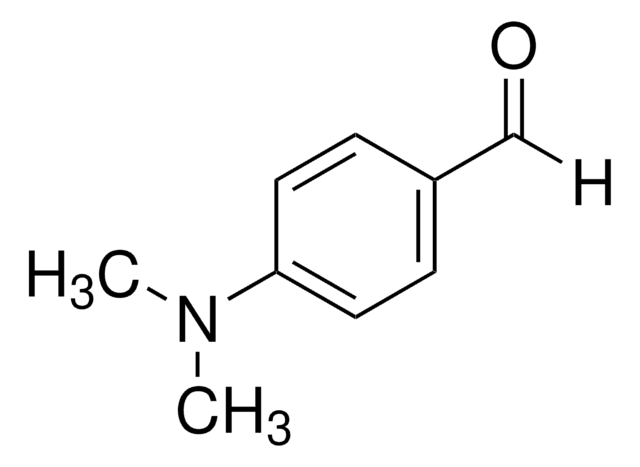
4-(dimethlyamino)benzaldehyde, 50 g/L
hydrochloric acid, 240 g/L
isoamylic alcohol, 710 g/L
técnica(s)
microbe id | specific enzyme detection: suitable
aplicação(ões)
agriculture
clinical testing
environmental
food and beverages
microbiology
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
adequação
Escherichia coli
coliforms
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
[H]C(=O)c1ccc(cc1)N(C)C
InChI
1S/C9H11NO/c1-10(2)9-5-3-8(7-11)4-6-9/h3-7H,1-2H3
chave InChI
BGNGWHSBYQYVRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Descrição geral
Aplicação
substituído por
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Órgãos-alvo
Respiratory system
Código de classe de armazenamento
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
109.4 °F
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
43 °C
Equipamento de proteção individual
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Artigos
An article regarding the Role of Clostridium perfringens and their detection, identification, and differentiation from Sigma-Aldrich.com
For microbiologists the most fundamental stain was developed in 1884 by the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram.
Sigma-Aldrich.com presents an article concerning Differentiation of Escherichia coli from coliforms.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica