SAE0158
Chitinase from Streptomyces griseus
chromatographically purified, lyophilized powder, free of DNA contaminants, suitable for Microbiome research
Synonym(s):
Chitinase from Streptomyces griseus, (1→4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucan glycanohydrolase), Chitodextrinase, Hydrolitic enzyme, Lytic Enzyme, Poly(β-(1→4)-[2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucoside]) glycanohydrolase, Poly(1,4-β-[2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucoside]) glycanohydrolase, beta-1,4-poly-N-acetyl glucosamidinase, poly-beta-glucosaminidase
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
specific activity
>200 USP units/mg solid
feature
DNA free
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
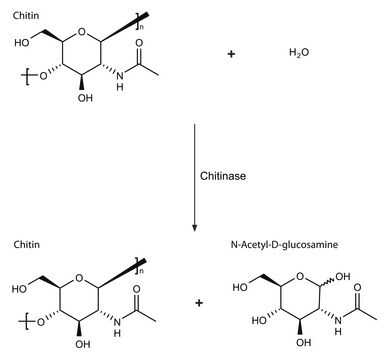
The enzymatic hydrolysis of chitin to N-acetyl-D-glucosamine involves two consecutive enzyme reactions:
- The first reaction, chitodextrinase-chitinase, is a poly(β-(1→4)-[2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucoside])- glycanohydrolase, which removes chitobiose units from chitin.
- The second activity is N-acetyl-glucosaminidasechitobiase, which cleaves the disaccharide to its monomer subunits, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine.
Application
- Agriculture fields: control pathogens.
- Human health care: Asthma.
- Pharma: preparation of chitooligosaccharides and N-acetyl D glucosamine,
- Preparation of single-cell protein
- Isolation of protoplasts from fungi and yeast
- Control of pathogenic fungi
- Treatment of chitinous waste, mosquito control and morphogenesis
Features and Benefits
Unit Definition
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Enzymes provide a non-mechanical method for cell lysis and protoplast preparation. It may seem like a simple process to throw in your enzyme, stick your tube in the water-bath and walk away, but what is actually going on in that process?
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service