R7397
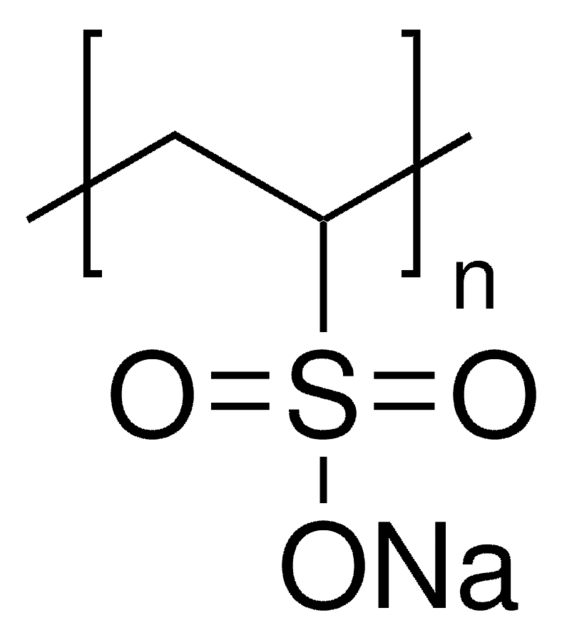
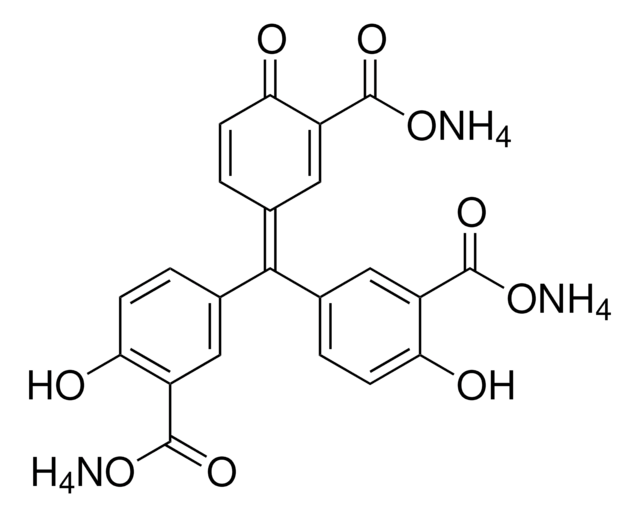
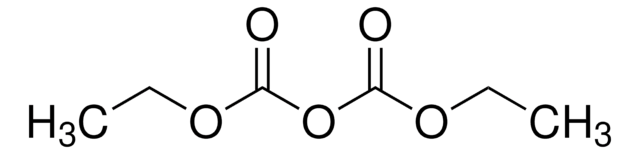
ProtectRNA™ RNase Inhibitor 500× Concentrate
RNase inhibitor for in situ hybridization assays
Synonym(s):
Ribonuclease inhibitor ProtectRNA™
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106300
NACRES:
NA.52
Recommended Products
General description
Not recommended in systems where other enzymatic activity is required.
ProtectRNA™ ribonuclease(RNase) Inhibitor inhibits most nucleic acid binding enzymes such as RNase and DNase, reverse transcriptase, some RNA and DNA polymerases, protein synthesis enzymes, and several restriction endonucleases. In contrast, ProtectRNA does not interfere with DNA and RNA hybridizations. The action ofProtectRNA as a nuclease inhibitor can be used as an advantage for in situ hybridization. ProtectRNA is useful during all steps of in situ hybridization for tissue RNA protection from RNase degradation. It is recommended to add ProtectRNA to all aqueous solutions used, from as early as the deparaffinization step until the hybridization is completed.
ProtectRNA™ ribonuclease(RNase) Inhibitor inhibits most nucleic acid binding enzymes such as RNase and DNase, reverse transcriptase, some RNA and DNA polymerases, protein synthesis enzymes, and several restriction endonucleases. In contrast, ProtectRNA does not interfere with DNA and RNA hybridizations. The action ofProtectRNA as a nuclease inhibitor can be used as an advantage for in situ hybridization. ProtectRNA is useful during all steps of in situ hybridization for tissue RNA protection from RNase degradation. It is recommended to add ProtectRNA to all aqueous solutions used, from as early as the deparaffinization step until the hybridization is completed.
Application
ProtectRNA™ RNase Inhibitor 500× Concentrate has been used in:
- RNA extraction
- tissue sectioning and staining for laser capture microscopy
- the isolation of blood vessels from hippocampi
ProtectRNA™ RNase Inhibitor 500× Concentrate is an RNase inhibitor.
A potent inhibitor of most nucleic acid binding enzymes, and thus useful as an RNase inhibitor. Especially useful when performing in situ hybridization. If it is added to all aqueous solutions used, it eliminates the need for special glassware washing and after-wash treatments. The 500x concentrate is economical; 2 ml treats 1,000 ml of solution. Not recommended in systems where other enzymatic activity is required.
Features and Benefits
- The 500× concentrate is economical
- Eliminates the need for special dishwashing and“after washing” cleaning and treatments.
Quantity
2mL treats 1,000ml of solution.
Other Notes
This product is for R&D use only, not for drug, household, or other uses.
Legal Information
ProtectRNA is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
signalword
Warning
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Liq. 3 - Met. Corr. 1
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
140.0 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
60 °C - closed cup
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Exposing the Three-Dimensional Biogeography and Metabolic States of Pathogens in Cystic Fibrosis Sputum via Hydrogel Embedding, Clearing, and rRNA Labeling.
DePas WH
mBio, 7(5), e00796-e00716 (2016)
Gene expression analysis of interferon kappa in laser capture microdissected cervical epithelium.
DeCarlo CA
Analytical Biochemistry, 381(1), 59-66 (2008)
Recovery of high-quality RNA from laser capture microdissected human and rodent pancreas.
Butler AE
Journal of Histotechnology, 39(2), 59-65 (2016)
Beatrice Quevedo et al.
BMC microbiology, 11, 14-14 (2011-01-21)
The purpose of this study was to design and evaluate fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) probes for the single-cell detection and enumeration of lactic acid bacteria, in particular organisms belonging to the major phylogenetic groups and species of oral lactobacilli
David Greenwood et al.
Proteomics. Clinical applications, 14(3), e2000011-e2000011 (2020-03-31)
Periodontitis is linked to a localized dysbiotic microbial shift. This trending may often not be evident due to deep taxonomic changes of low abundance organisms and lack of consideration of variations in the treatment response. By using next generation sequencing
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service