N2635
Nucleoside 5′-Diphosphate Kinase from bovine liver
buffered aqueous glycerol solution, ≥1,000 units/mg protein (biuret)
Synonym(s):
NDK, UDPkinase, nonmetastatic23(NM23), uridine diphosphate kinase, ATP:nucleoside diphosphate phosphotransferase, NDPK
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
eCl@ss:
32160410
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine liver
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
specific activity
≥1,000 units/mg protein (biuret)
storage condition
(Tightly closed)
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
foreign activity
lactic dehydrogenase, myokinase, β-NADH oxidase, nucleoside monophosphokinase and ATPase ≤0.1%
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Research area: Cell Signaling
Nucleoside 5′-Diphosphate Kinase (NDK) is a ubiquitous housekeeping enzyme. Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase exists in two isoforms in eukaryotic cells, NDK-A and NDK-B. These enzymes are found expressed both in the mitochondria and the cytoplasm.
Nucleoside 5′-Diphosphate Kinase (NDK) is a ubiquitous housekeeping enzyme. Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase exists in two isoforms in eukaryotic cells, NDK-A and NDK-B. These enzymes are found expressed both in the mitochondria and the cytoplasm.
Application
Nucleoside 5′-Diphosphate Kinase has been used:
- nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) assays
- coupled NDPK-luciferase assay to determine the amounts of Ras-bound guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
- non-metastatic protein 23 (NM23) growth stimulation assay
- in a study to assess inhibition of type I Fc epsilon receptor mediated Ca2+ influx and mediator secretion in rat mucosal mast cells
- in a study to investigate protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nucleoside 5′-Diphosphate Kinases (NDKs) aid in the synthesis of nucleoside triphosphates (NTPs) by transferring a phosphate group from ATP to nucleoside diphosphates (NDPs). NDKs provide NTPs for nucleic acid synthesis, cytidine 5′-triphosphate (CTP) for lipid synthesis, uridine 5′-triphosphate (UTP) for polysaccharide synthesis, and guanosine triphosphate (GTP) for protein elongation, signal transduction, and microtubule polymerization.
Unit Definition
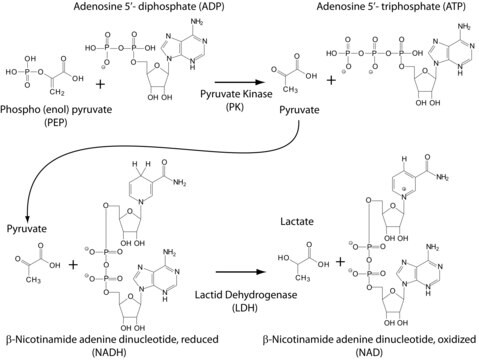
One unit will convert 1.0 μmole each of TDP and ATP to TTP and ADP per min at pH 7.6 at 25 °C in a coupled system with PK/LDH.
Related product
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Substrate
antibody
enzyme
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Maja Herak Bosnar et al.
Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 329(1-2), 63-71 (2009-04-18)
The family of Nm23/NDPK (nucleoside diphosphate kinase) proteins regulates a vast variety of cellular processes and, therefore, participates in important physiological events like proliferation, differentiation, molecular transport, and apoptosis. The majority of experimental data concerning this gene family has been
Krisztina Takács-Vellai et al.
Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 72(8), 1447-1462 (2014-12-30)
In textbooks of biochemistry, nucleoside diphosphate conversion to a triphosphate by nucleoside diphosphate 'kinases' (NDPKs, also named NME or NM23 proteins) merits a few lines of text. Yet this essential metabolic function, mediated by a multimeric phosphotransferase protein, has effects
Shaobai Huang et al.
Annals of botany, 96(4), 703-715 (2005-07-20)
Anoxia-tolerant plant tissues synthesize a number of proteins during anoxia, in addition to the 'classical anaerobic proteins' involved in glycolysis and fermentation. The present study used a model system of rice coleoptile tips to elucidate patterns of protein synthesis in
S Hemmerich et al.
Biochemistry, 30(6), 1523-1532 (1991-02-12)
Type I Fc epsilon receptor (Fc epsilon RI) mediated Ca2+ uptake and secretion of rat serosal mast cells have been shown to be inhibited by disodium 1,3-bis [(2'-carboxylatochromon-5'-yl) oxy]-2-hydroxypropane (disodium cromoglycate, DSCG), which is widely employed in the treatment of
Sanjeev Mahanta et al.
PloS one, 3(4), e2054-e2054 (2008-05-01)
The MUC1 protein is aberrantly expressed on many solid tumor cancers. In contrast to its apical clustering on healthy epithelial cells, it is uniformly distributed over cancer cells. However, a mechanistic link between aberrant expression and cancer has remained elusive.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service