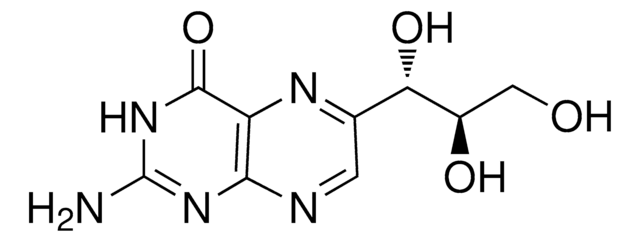
M4758
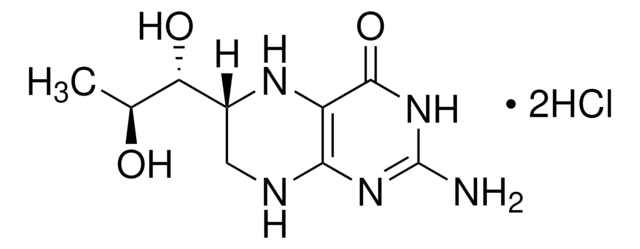
(±)-6-Methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterine dihydrochloride
~95% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
6-MPH4, DL-2-Amino-4-hydroxy-6-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridine dihydrochloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C7H11N5O · 2HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
254.12
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
5648114
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.51
assay:
~95% (TLC)
Recommended Products
assay
~95% (TLC)
Quality Level
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.Cl.CC1CNc2nc(N)nc(O)c2N1
InChI
1S/C7H11N5O.2ClH/c1-3-2-9-5-4(10-3)6(13)12-7(8)11-5;;/h3,10H,2H2,1H3,(H4,8,9,11,12,13);2*1H
InChI key
MKQLORLCFAZASZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
6-MPH4 is used to study mechanisms of nitric oxide (NO) synthase and free radical induced L-DOPA release from striatal tissue.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Synthetic cofactor for tyrosine hydrolase; also cofactor for phenylalanine and tryptophan hydroxylases; less activity than the natural cofactor, BH4
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Elizabeth A Gaskell et al.
PloS one, 4(3), e4801-e4801 (2009-03-12)
The genome of the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii was found to contain two genes encoding tyrosine hydroxylase; that produces L-DOPA. The encoded enzymes metabolize phenylalanine as well as tyrosine with substrate preference for tyrosine. Thus the enzymes catabolize phenylalanine to
P Abreu-González et al.
European journal of pharmacology, 541(1-2), 33-37 (2006-06-06)
In the present study we have analyzed the effect of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) essential cofactor for tyrosine hydroxylase and nitric oxide synthase, on the 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) release from in vitro incubated striatal tissue. dl-6-methyl-5,6,7,8 tetrahydropterine (6-MPH4)-stimulated L-DOPA release in a concentration-dependent
M Bauer et al.
Journal of neurochemistry, 82(5), 1300-1310 (2002-10-03)
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) protects dopaminergic neurones against toxic and physical damage. In addition, GDNF promotes differentiation and structural integrity of dopaminergic neurones. Here we show that GDNF can support the function of primary dopaminergic neurones by triggering
J R Bostwick et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 192(1), 125-130 (1991-01-01)
A radiometric assay for tyrosine hydroxylase employing a coupled nonenzymatic decarboxylation of L-[14C]Dopa formed from L-[14C]tyrosine has been adapted for performance in a 96 microwell culture plate. The method uses an easily manufactured plate holder to compress blotting paper impregnated
F García-Molina et al.
Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1794(12), 1766-1774 (2009-08-22)
There is controversy in the literature concerning the action of tetrahydropterines on the enzyme tyrosinase and on melanogenesis in general. In this study, we demonstrate that tetrahydropterines can inhibit melanogenesis in several ways: i) by non-enzymatic inhibition involving purely chemical
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service