B1814
BMP2, human
Carrier Free, ≥98% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
BMP-2
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 human, Carrier Free, ≥98% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
assay
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
mol wt
26 kDa
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles (Do not store in a frost-free freezer.)
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
Endotoxin, tested
color
white
solubility
water: soluble 0.100 mL, clear, colorless
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... BMP2(650)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
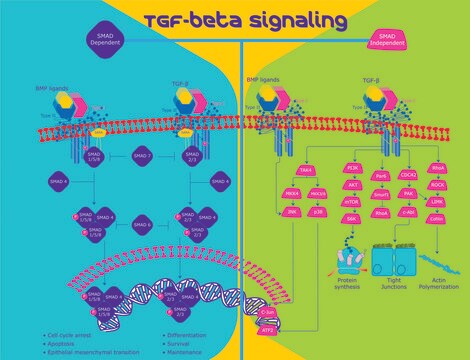
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Analysis Note
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
104.0 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
40.0 °C - closed cup
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service