450197
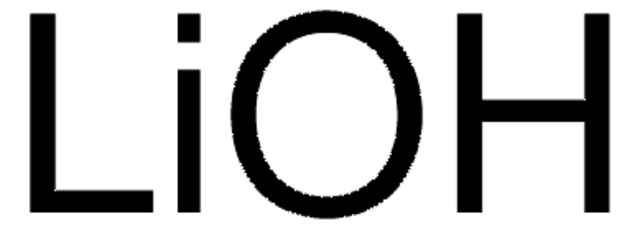
Lithium hydroxide monohydrate
99.995% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Lithium hydroxide hydrate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
LiOH · H2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
41.96
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352302
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
assay
99.995% trace metals basis
form
solid
impurities
≤55.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
SMILES string
[Li+].O.[OH-]
InChI
1S/Li.2H2O/h;2*1H2/q+1;;/p-1
InChI key
GLXDVVHUTZTUQK-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Lithium hydroxide monohydrate, 99.995% trace metals basis is a white colored salts. We offer highly pure and controlled specifications to fulfill research needs such as enhancing battery technology and improving lubricants to ensuring air quality in closed environments, and contributing to advanced materials in glass, ceramics, and polymers.
Application
Lithium hydroxide monohydrate (LiOH⋅H2O) is a crucial precursor for the production of lithium-ion battery cathode material such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC). Lithium hydroxide monohydrate is used in CO2 scrubbers to absorb carbon dioxide from the air. This application is crucial in closed environments such as submarines, spacecraft, and underwater habitats. Lithium hydroxide monohydrate can be used as a catalyst. In a recent study, it has been found that Lithium hydroxide monohydrate works as a novel catalyst for Knoevenagel condensation of aryl aldehydes with malononitrle and ethylcyanoacetate. Also it is used as highly efficient catalyst for Gewald reaction, for an easy and highly efficient synthesis of arylidene malononitrile,arylidene ethylcyanoacetate and 2-aminthiophenes.
Features and Benefits
The following benefits are the main feature of the product:
- requirement of a small amount while using as a catalyst,
- short reaction times, and
- high product yields etc
- Low trace metals content ( < 55.0 ppm)
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Preparation of high-purity lithium hydroxide monohydrate from technical-grade lithium carbonate by membrane electrolysis
Ryabtsev AD, et al.
Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 77(7), 1108-1116 (2004)
Precipitation in aqueous lithium-oxygen batteries: a model-based analysis
Horstmann B, et al.
Energy & Environmental Science, 6(4), 1299-1314 (2013)
Preparation and performances of highly porous layered LiCoO2 films for lithium batteries.
Koike S and Tatsumi K.
Journal of Power Sources, 174(2), 976-980 (2007)
Maria Concetta Bruzzoniti et al.
Journal of chromatography. A, 1187(1-2), 188-196 (2008-02-29)
A new high performance ion chromatographic method has been developed for the separation of the nine chlorinated-brominated haloacetic acids (HAAs) that are the disinfection by-products of chlorination of drinking water, using a macrocycle-based adjustable-capacity anion-exchange separator column (IonPac Cryptand A1).
Kwang-Heon Kim et al.
Ultrasonics sonochemistry, 15(6), 1019-1025 (2008-05-09)
Nano-sized HT-LiCoO(2) powders were prepared by sonochemical synthesis in an aqueous solution of lithium hydroxide containing cobalt hydroxide at approximately 80 degrees C without any further heat treatment at high temperature. The effects of the LiOH concentration, oxidation conditions, ultrasound
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service