440914
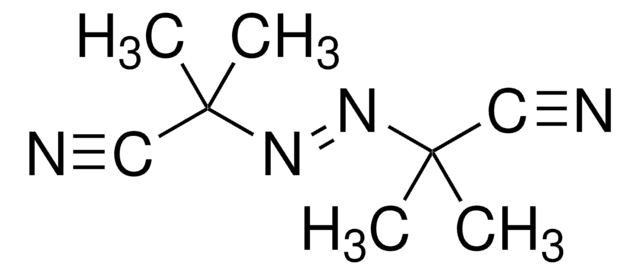
2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride
powder or granules, 97%
Synonym(s):
α,α′-Azodiisobutyramidine dihydrochloride, AAPH
About This Item
Recommended Products
assay
97%
form
powder or granules
t1/2
10 hr(56 °C)
mp
175-177 °C (lit.)
solubility
acetone, dioxane, methanol, ethanol, DMSO and water: soluble
SMILES string
Cl.Cl.CC(C)(\N=N\C(C)(C)C(N)=N)C(N)=N
InChI
1S/C8H18N6.2ClH/c1-7(2,5(9)10)13-14-8(3,4)6(11)12;;/h1-4H3,(H3,9,10)(H3,11,12);2*1H/b14-13+;;
InChI key
LXEKPEMOWBOYRF-QDBORUFSSA-N
Related Categories
Application
Polymerization initiator for acrylic, vinyl and allyl monomers.
Features and Benefits
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Self-heat. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class
4.2 - Pyrophoric and self-heating hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
We presents an article about Copper(I)-mediated Living Radical Polymerization in the Presence of Pyridylmethanimine Ligands, and the emergence of living radical polymerization mediated by transition metal catalysts in 1995, which was a seminal piece of work in the field of synthetic polymer chemistry.
Applying ARGET ATRP to the Growth of Polymer Brush Thin Films by Surface-initiated Polymerization
Protocols
Monodisperse, surfactant-free polymer spheres for use as colloidal crystal templates can be easily obtained in reasonably large quantities. Typical synthesis methods for poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) and poly(styrene) (PS) by emulsifier free emulsion polymerization are described below and yield spheres several hundred nanometers in diameter.
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service