C9322
Catalase from bovine liver
lyophilized powder, 2,000-5,000 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
H2O2:H2O2 oxidoreductase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine liver
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
2,000-5,000 units/mg protein
mol wt
tetramer ~250 kDa
isoelectric point
5.4
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
O(CC)C(=O)c1ccc(cc1)O
InChI
1S/C9H10O3/c1-2-12-9(11)7-3-5-8(10)6-4-7/h3-6,10H,2H2,1H3
InChI key
NUVBSKCKDOMJSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
cow ... CAT(280743)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Catalase from bovine liver is a tetramer consisting of 4 equal subunits each with a 60 kDa molecular weight. Each of these subunits contains iron bound to a protoheme IX group. The enzyme will also strongly bind to NADP, where NADP and the heme group are within 13.7 angstroms.
Application
Catalase from bovine liver may be used:
- to prepare H2O2-O2 based biocathode for applications in glucose biofuel cells
- to study the kinetic properties and storage stability of catalase immobilized on to florisil
- in glutathione-mediated superoxide generation in an aqueous solution
Biochem/physiol Actions
Caution
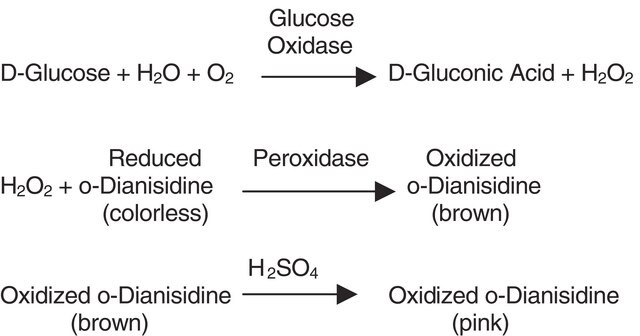
Unit Definition
Preparation Note
The enzyme is soluble in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer at 1 mg/mL and pH 7.0.
Storage and Stability
inhibitor
signalword
Danger
hcodes
pcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
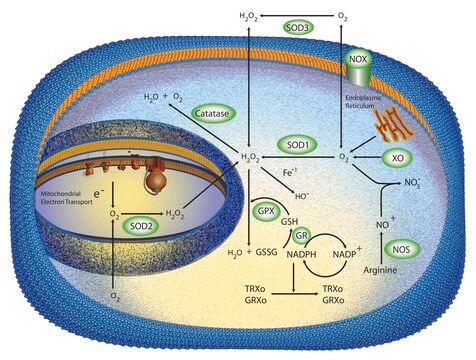
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service