Key Documents
P1431
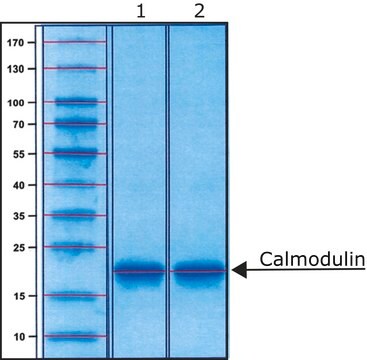
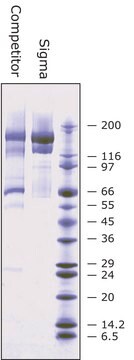
Calmodulin from bovine testes
BioUltra, ≥98% (SDS-PAGE), lyophilized powder, essentially salt free
Synonim(y):
CaM, Phosphodiesterase 3′:5′-cyclic nucleotide activator
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
bovine testis
Poziom jakości
linia produktu
BioUltra
Próba
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
Postać
lyophilized powder
masa cząsteczkowa
16.79 kDa
warunki przechowywania
(Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place)
metody
ligand binding assay: suitable
zanieczyszczenia
salt, essentially free
numer dostępu UniProt
Zastosowanie
cell analysis
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
informacje o genach
cow ... CALM3(520277)
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Calmodulin (CaM) is a Ca2+-sensor protein containing four EF-hand motifs that bind to four Ca2+ ions. It is found ubiquitously in all eukaryotes.
Zastosowanie
- as a component of the reaction mixture in PhosphoSens assay to measure Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II α (CaMKIIα) substrate phosphorylation
- to generate standard curve for the determination of in situ calmodulin concentration in tissues
- as a ligand in radio-ligand binding for studying calmodulin affinity
Działania biochem./fizjol.
produkt powiązany
przeciwciało
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej