Kluczowe dokumenty
P0358
Anti-Potassium Channel Kv4.3 antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, lyophilized powder
Synonim(y):
Anti-BRGDA9, Anti-KCND3L, Anti-KCND3S, Anti-KSHIVB, Anti-KV4.3, Anti-SCA19, Anti-SCA22
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
rabbit
Poziom jakości
białko sprzężone
unconjugated
forma przeciwciała
affinity isolated antibody
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
polyclonal
Postać
lyophilized powder
reaktywność gatunkowa
rat, human
metody
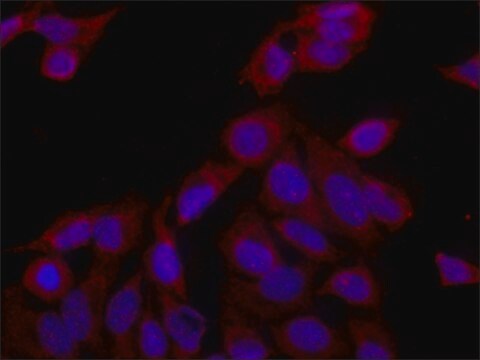
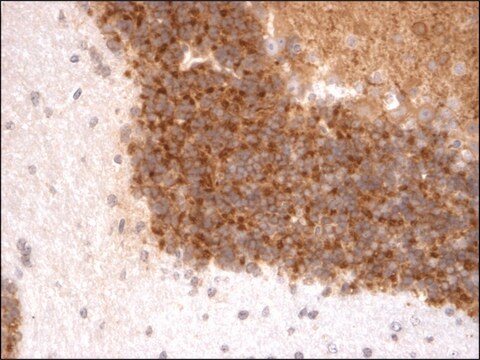
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): suitable
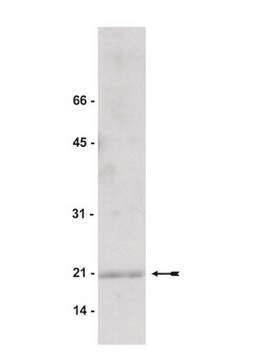
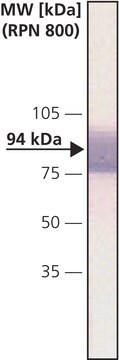
western blot (chemiluminescent): 1:200
numer dostępu UniProt
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
docelowa modyfikacja potranslacyjna
unmodified
informacje o genach
human ... KCND3(3752)
rat ... Kcnd3(65195)
Opis ogólny
Immunogen
Zastosowanie
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Postać fizyczna
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Aquatic Chronic 3
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej