Wszystkie zdjęcia(1)
Kluczowe dokumenty
F4042
Monoclonal ANTI-FLAG® M5 antibody produced in mouse
clone M5, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution
Synonim(y):
Anti-ddddk, Anti-dykddddk
Zaloguj sięWyświetlanie cen organizacyjnych i kontraktowych
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
mouse
białko sprzężone
unconjugated
forma przeciwciała
purified immunoglobulin
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
M5, monoclonal
Formularz
buffered aqueous solution
oczyszczone przez
using Protein A
reaktywność gatunkowa
all
stężenie
2-5 mg/mL
metody
western blot (chemiluminescent): 10 μg/mL
izotyp
IgG1
sekwencja immunogenna
DYKDDDDK
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
Opis ogólny
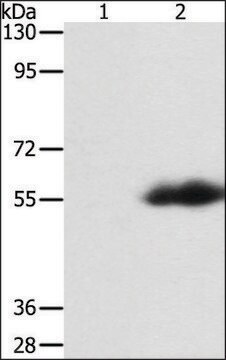
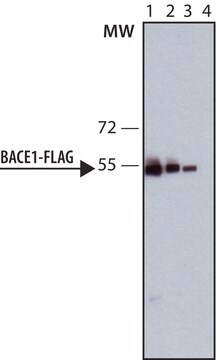
Monoclonal ANTI-FLAG® M5 is a mouse antibody that binds to N-terminal Met-FLAG fusion proteins. It is useful for detection of N-terminal Met-FLAG fusion proteins expressed in mammalian and Drosophilae cells.
Method of purification - Protein A
Method of purification - Protein A
Immunogen
FLAG; peptide sequence DYKDDDDK
Zastosowanie
Binds the FLAG peptide only when it is located at the amino terminus preceded by a methionine. Binding is not Ca2+-dependent. Useful for detecting cytoplasmically expressed Met-FLAG fusion proteins in mammalian crude cell extracts, but not recommended for fusion proteins expressed in E. coli.
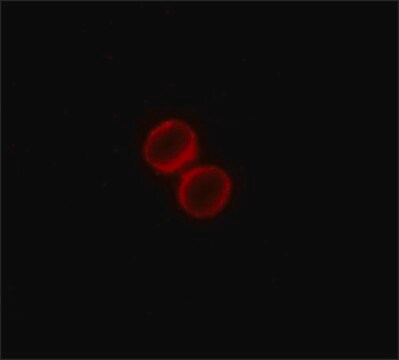
Monoclonal ANTI-FLAG® M5 antibody produced in mouse has been used in western blotting and immunofluorescence.
Postać fizyczna
Solution in 10 mM sodium phosphate, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4, containing 0.02% sodium azide (w/v)
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
Dilute the antibody to 10 mg/mL in Tris buffered saline (TBS): 0.05 M Tris, 0.15 M NaCl, pH 7.4.
Inne uwagi
Antibody is not calcium dependent.
Informacje prawne
ANTI-FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
nwg
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
DEF-1/ASAP1 is a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for ARF1 that enhances cell motility through a GAP-dependent mechanism
Furman C, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(10), 7962-7969 (2002)
Bader Almuzzaini et al.
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 30(8), 2860-2873 (2016-04-30)
Actin and nuclear myosin 1 (NM1) are regulators of transcription and chromatin organization. Using a genome-wide approach, we report here that β-actin binds intergenic and genic regions across the mammalian genome, associated with both protein-coding and rRNA genes. Within the
Chih-Chao Liang et al.
Nature communications, 7, 12124-12124 (2016-07-14)
The Fanconi anaemia (FA) pathway is important for the repair of DNA interstrand crosslinks (ICL). The FANCD2-FANCI complex is central to the pathway, and localizes to ICLs dependent on its monoubiquitination. It has remained elusive whether the complex is recruited
Franz Oswald et al.
Nucleic acids research, 44(10), 4703-4720 (2016-02-26)
The transcriptional shift from repression to activation of target genes is crucial for the fidelity of Notch responses through incompletely understood mechanisms that likely involve chromatin-based control. To activate silenced genes, repressive chromatin marks are removed and active marks must
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta regulates the repression of type II collagen expression during the differentiation from proliferative to hypertrophic chondrocytes
Ushijima T, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(5), 2852-2863 (2014)
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej