Kluczowe dokumenty
A9539
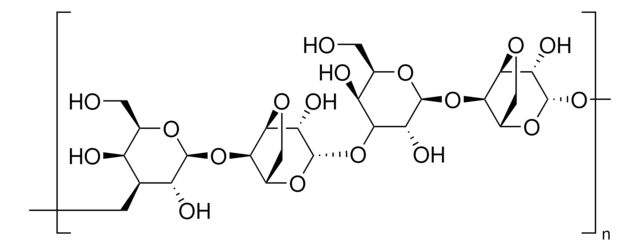
Agarose
BioReagent, for molecular biology, low EEO
Synonim(y):
3,6-Anhydro-α-L-galacto-β-D-galactan, Agarose LE
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
algae (marine)
Poziom jakości
klasa czystości
for molecular biology
linia produktu
BioReagent
Formularz
powder
metody
electrophoresis: suitable
zanieczyszczenia
≤10% moisture content
EEO
0.09-0.13
temp. przejścia
gel point 36 °C ±1.5 °C (1.5% gel)
siła żelu
≥1200 g/cm2 (1% gel)
ślady anionów
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.15%
przydatność
suitable for electrophoresis
suitable for molecular biology
obecność zanieczyszczeń
DNase, RNase, none detected
ciąg SMILES
O1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]([C@H]1CO)O)O[C@@H]4O[C@@H]5[C@H]([C@@H](OC5)[C@@H]4O)O[C@@H]6O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H]6O)O)O)CO)O)O[C@H]2[C@H]3OC[C@@H]2O[C@H]([C@H]3O)O
InChI
1S/C24H38O19/c25-1-5-9(27)11(29)12(30)22(38-5)41-17-8-4-36-20(17)15(33)24(40-8)43-18-10(28)6(2-26)39-23(14(18)32)42-16-7-3-35-19(16)13(31)21(34)37-7/h5-34H,1-4H2/t5-,6-,7+,8+,9+,10+,11+,12-,13+,14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20+,21-,22+,23+,24+/m1/s1
Klucz InChI
MJQHZNBUODTQTK-WKGBVCLCSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- in gel electrophoresis to analyze the integrity of DNA
- to prepare hydrocolloid gels and study the structural influence of gels on the release of carbohydrates
- in gel electrophoresis to analyze the integrity of RNA
- it is suitable for protein applications such as Ouchterlony and radial immunodiffusion (RID)
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Cechy i korzyści
- Biocompatible
- Agarose gels have larger pore sizes than polyacrylamide gels at low concentrations
- Unlike polyacrylamide, the consistency of the gels is more solid (but also less elastic)
- Possesses low ethidium bromide and SYBR Green background staining
Komentarz do analizy
Sulfate content - used as an indicator of purity, since sulfate is the major ionic group present.
Gel strength - the force that must be applied to a gel to cause it to fracture.
Gel point - the temperature at which an aqueous agarose solution forms a gel as it cools. Agarose solutions exhibit hysteresis in the liquid-to-gel transition - that is, their gel point is not the same as their melting temperature.
Electroendosmosis (EEO) - a movement of liquid through the gel. Anionic groups in an agarose gel are affixed to the matrix and cannot move, but dissociable counter cations can migrate toward the cathode in the matrix, giving rise to EEO. Since electrophoretic movement of biopolymers is usually toward the anode, EEO can disrupt separations because of internal convection.
Inne uwagi
najczęściej kupowane z tym produktem
produkt podobny
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Protokoły
The GenElute Blood Genomic DNA Kit Protocol provides a simple and convenient way to isolate pure genomic DNA from fresh or aged whole blood.
The GenElute Mammalian Genomic DNA Purification Kit Protocol describes the isolation of pure, high molecular weight DNA from a variety of mammalian sources.
Protokół zestawu do oczyszczania genomowego DNA ssaków GenElute opisuje izolację czystego DNA o wysokiej masie cząsteczkowej z różnych źródeł ssaków.
GenElute Bacterial Genomic DNA Kit protocol describes a simple and convenient way for the isolation of pure genomic DNA from bacteria.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej