Kluczowe dokumenty
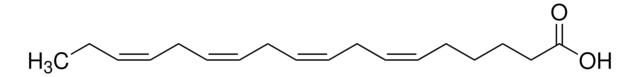
A3611
Arachidonic acid
from non-animal source, ≥98.5% (GC)
Synonim(y):
cis,cis,cis,cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid, Eicosa-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-tetraenoic acid, Immunocytophyte
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
non-animal source
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥98.5% (GC)
Formularz
liquid
współczynnik refrakcji
n20/D 1.4872 (lit.)
bp
169-171 °C/0.15 mmHg (lit.)
mp
−49 °C (lit.)
gęstość
0.922 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
grupa funkcyjna
carboxylic acid
typ lipidu
omega FAs
Warunki transportu
dry ice
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
ciąg SMILES
OC(CCC/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCC)=O
InChI
1S/C20H32O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20(21)22/h6-7,9-10,12-13,15-16H,2-5,8,11,14,17-19H2,1H3,(H,21,22)/b7-6-,10-9-,13-12-,16-15-
Klucz InChI
YZXBAPSDXZZRGB-DOFZRALJSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
<li><strong>Molekularne mechanizmy związane z hamującą rolą długołańcuchowych n-3 PUFA w raku jelita grubego:</strong> Niniejsze badanie omawia wpływ długołańcuchowych wielonienasyconych kwasów tłuszczowych, takich jak kwas arachidonowy, na mechanizmy raka jelita grubego. Badania koncentrują się na roli przeciwzapalnej i hamującej raka poprzez modulację metabolizmu lipidów i szlaków transdukcji sygnału (Jayathilake et al., 2024).</li>
<li><strong>Zhilining Formula łagodzi zapalenie jelita grubego wywołane przez DSS poprzez hamowanie stanu zapalnego i dysfunkcji bariery jelitowej poprzez oś AHR/NF-Bp65:</strong> W artykule przedstawiono rolę kwasu arachidonowego w hamowaniu stanu zapalnego i przywracaniu funkcji bariery jelitowej, co ma kluczowe znaczenie dla zrozumienia chorób zapalnych i opracowania strategii terapeutycznych (Zhou et al., 2024).</li>
<li><strong>Lakton 5,6-diHETE (EPA-L) pośredniczy w nadciśnieniowym rozszerzeniu mikronaczyń poprzez aktywację śródbłonkowego szlaku sygnałowego GPR-PLC-IP(3):</strong> Bada konsekwencje sercowo-naczyniowe metabolitów kwasu arachidonowego, w szczególności ich rolę w reakcjach mikronaczyniowych, co może wpłynąć na strategie leczenia nadciśnienia (Asulin et al., 2024).</li>
</ul>.
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Opakowanie
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej