Key Documents
91957
Monosodium methylphosphonate
99.0-101.0% (T)
Synonim(y):
Methanephosphonic acid monosodium salt, Methylphosphonic acid monosodium salt
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
99.0-101.0% (T)
Postać
crystals
stężenie
18.5-20.5% Na
strata
≤2.0% loss on drying
pH
4.5-5.1
rozpuszczalność
water: 3.54 g/30 mL, colorless
ślady kationów
Al: ≤5 mg/kg
Ba: ≤5 mg/kg
Bi: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤50 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Mo: ≤5 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Sr: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
absorpcja UV
λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.2
λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.07
przydatność
no residue for filter test
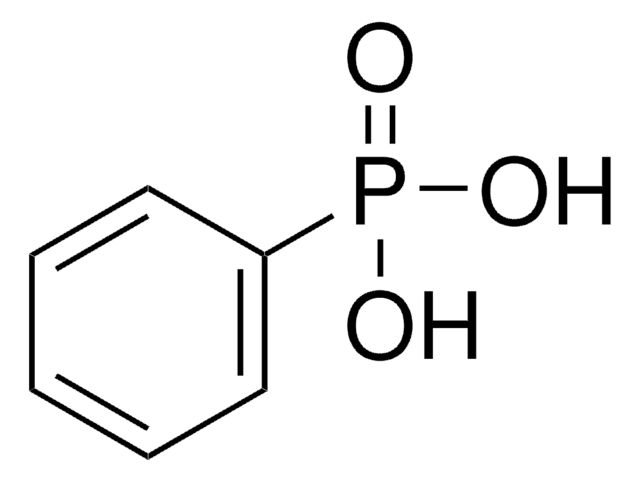
ciąg SMILES
O=P(C)(O[Na])O
InChI
1S/CH5O3P.Na/c1-5(2,3)4;/h1H3,(H2,2,3,4);/q;+1/p-1
Klucz InChI
CZVWTNTXBUVAFR-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Zastosowanie
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Kod klasy składowania
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej