Kluczowe dokumenty
53747
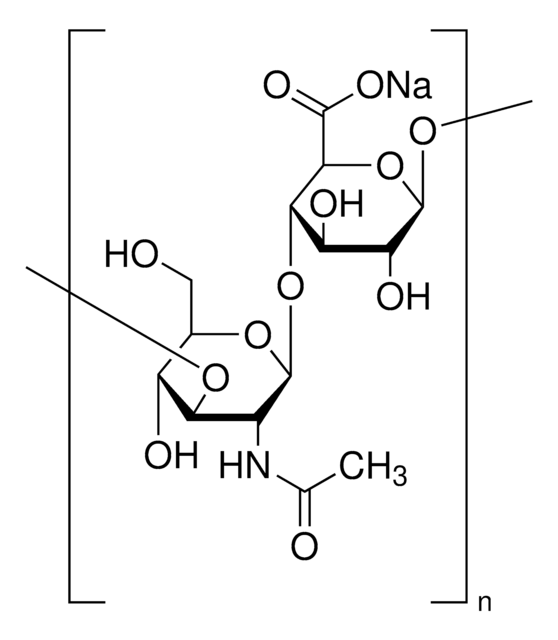
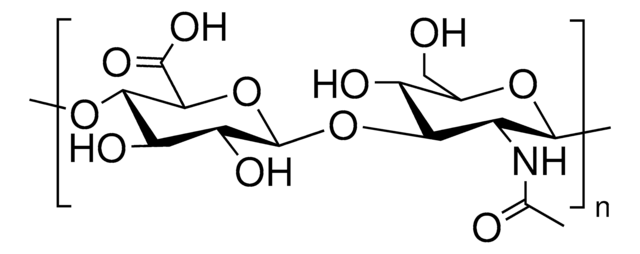
Hyaluronic acid sodium salt from Streptococcus equi
bacterial glycosaminoglycan polysaccharide
Synonim(y):
Poly(β-glucuronic acid-[1→3]-β-N-acetylglucosamine-[1→4]), alternating
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
(Streptococcus equi)
Formularz
powder or crystals
masa cząsteczkowa
~1.5-1.8 x 10E6 Da
zanieczyszczenia
≤1% protein
kolor
white
rozpuszczalność
H2O: 5 mg/mL, clear, colorless
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
ciąg SMILES
[Na+].CC(=O)N[C@@H]1C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)O[C@@H]2C([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C28H44N2O23.Na/c1-5(33)29-9-18(11(35)7(3-31)47-25(9)46)49-28-17(41)15(39)20(22(53-28)24(44)45)51-26-10(30-6(2)34)19(12(36)8(4-32)48-26)50-27-16(40)13(37)14(38)21(52-27)23(42)43;/h7-22,25-28,31-32,35-41,46H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H,29,33)(H,30,34)(H,42,43)(H,44,45);/q;+1/t7-,8-,9-,10-,11-,12-,13+,14+,15-,16-,17-,18-,19-,20+,21+,22+,25-,26+,27-,28-;/m1./s1
Klucz InChI
YWIVKILSMZOHHF-QJZPQSOGSA-N
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- with methacrylic anhydride for synthesizing cross-linkable methacrylated HA hydrogel (Coll-MeHA)
- in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) to replace the PBS bath to vary the lubricant composition
- in the preparation of lubricant to study its effects on the boundary lubrication of human osteoarthritis (OA) cartilage
Działania biochem./fizjol.
Inne uwagi
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Dowiedz się więcej o glikozoaminoglikanach i proteoglikanach, w tym o strukturze glikozoaminoglikanów (GAG), różnych typach GAG i ich funkcjach.
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej