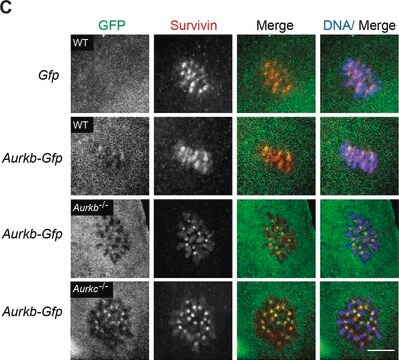
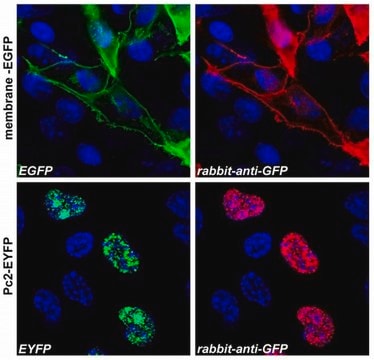
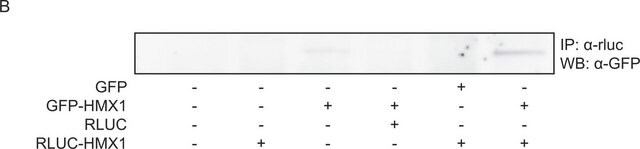
Kluczowe dokumenty
11814460001
Roche
Anti-GFP
from mouse IgG1κ (clones 7.1 and 13.1)
Synonim(y):
anti-green fluorescent protein
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
mouse
Poziom jakości
białko sprzężone
unconjugated
forma przeciwciała
purified immunoglobulin
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
13.1, monoclonal
7.1, monoclonal
Próba
>90% (HPLC)
Postać
lyophilized
opakowanie
pkg of 200 μg
producent / nazwa handlowa
Roche
izotyp
IgG1κ
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
Opis ogólny
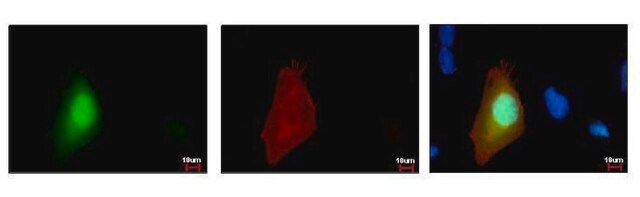
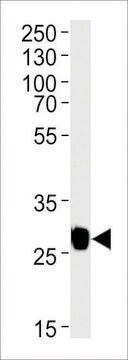
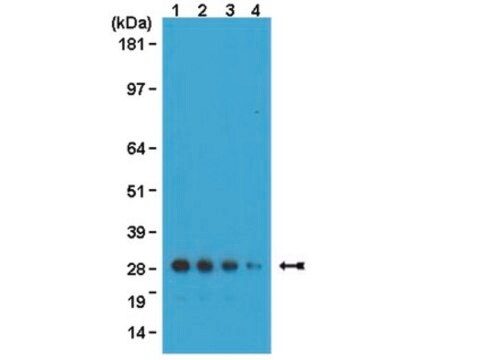
Specyficzność
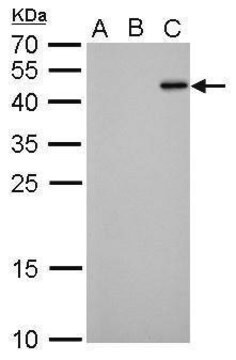
Zastosowanie
- Immunoprecipitation
- Western blots
- Immunostaining
Cechy i korzyści
Mixture of two monoclonal antibodies, supplied as a white lyophilizatecontaining 200μg of total Anti-GFP IgG.
Anti-GFP is a mixture of two clones (7.1 and 13.1).
Jakość
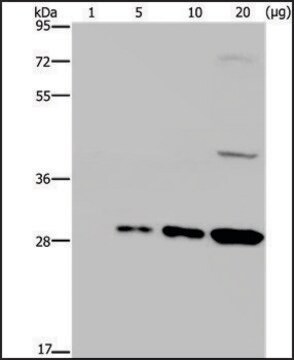
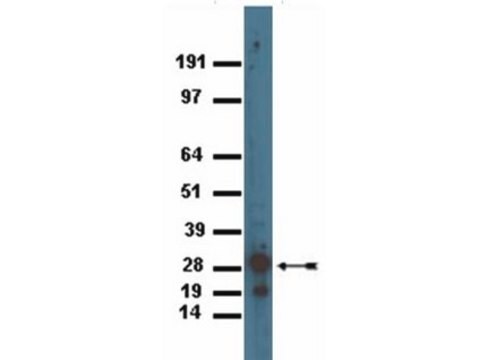
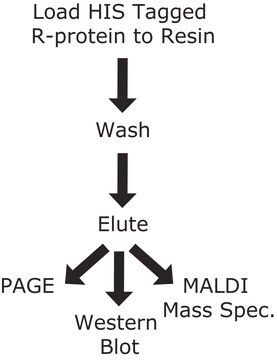
Purity: Both Anti-GFP mouse monoclonal antibodies (Clones 7.1 and 13.1) are >95% pure as determined by SDS-PAGE and ion-exchange HPLC analyses.
Uwaga dotycząca przygotowania
The following concentrations should be taken as a guideline:
- Western blot: 1:1000 dilution
- Immunoprecipitation: 2 to 10 μg
Storage conditions (working solution): -15 to -25 °C
Rekonstytucja
Rehydrate on ice for 30 minutes.
Informacje prawne
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Kod klasy składowania
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
does not flash
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
does not flash
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej