MABE1095
Anti-DNA-RNA Hybrid Antibody, clone S9.6
clone S9.6, from mouse
Synonim(y):
DNA-RNA Duplex, DNA/RNA Duplex, DNA:RNA Duplex, DNA-RNA Hybrid, DNA/RNA Hybrid, DNA:RNA Hybrid, RNA-DNA Duplex, RNA/DNA Duplex, RNA:DNA Duplex, RNA-DNA Hybrid, RNA/DNA Hybrid, RNA:DNA Hybrid
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
mouse
Poziom jakości
forma przeciwciała
purified immunoglobulin
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
S9.6, monoclonal
reaktywność gatunkowa (przewidywana na podstawie homologii)
all
metody
ChIP: suitable
affinity binding assay: suitable
dot blot: suitable
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
izotyp
IgG2aκ
Warunki transportu
ambient
docelowa modyfikacja potranslacyjna
unmodified
Opis ogólny
Specyficzność
Immunogen
Zastosowanie
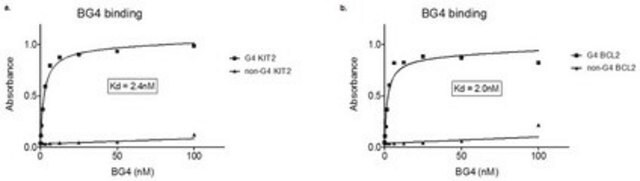
Affinity Binding Assay: Clone S9.6 bound the DNA-RNA heteropolymer and poly(I)-poly(dC) equally, but 100-fold higher levels of poly(A)-poly(dT) were required to achieve a similar degree of binding. Single-stranded DNA, double-stranded DNA and RNA, and ribosomal RNA were not bound by clone S9.6 (Boguslawski, S.J., et al. (1986). J. Immunol Methods. 89(1):123-130).
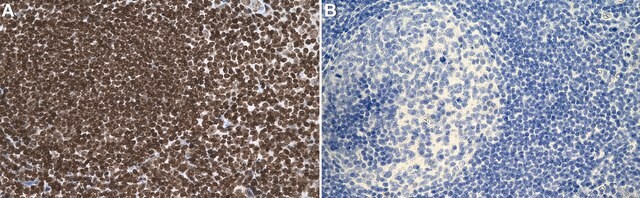
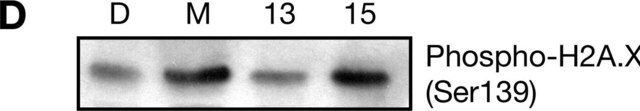
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Analysis: A representative lot detected increased DNA RNA hybrids at four actively transcribed genes upon shRNA-mediated knockdown of BRCA1 or BRCA2, but not PCID2 or RAD51 in HeLa cells (Bhatia, V., et al. (2014). Nature. 511(7509):362-365).
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Analysis: A representative lot detected R-loops formed over beta-actin gene using HeLa chromatin preparation. RNase H treatment of the chromatin preparation prevented clone S9.6 from immunoprecipitating target chromatin fragments (Skourti-Stathaki, K., et al. (2011). Mol. Cell. 42(6):794-805).
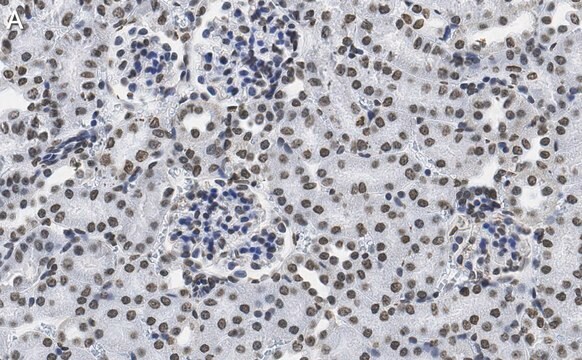
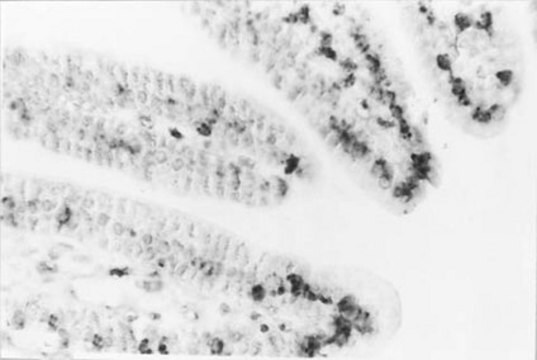
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation-sequencing (ChIP-seq) Analysis: A representative lot detected genome-wide distribution of DNA-RNA hybrids in budding yeast by ChIP-seq analysis (El Hage, A., et al. (2014). PLoS Genet. 10(10):e1004716).
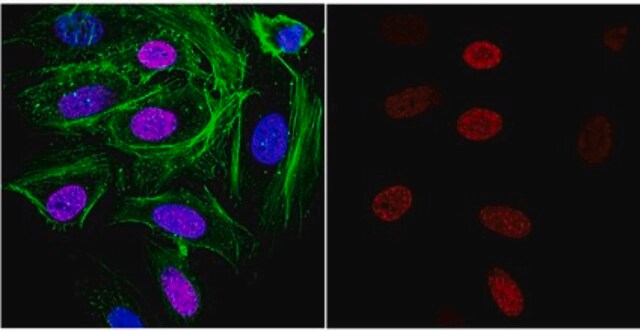
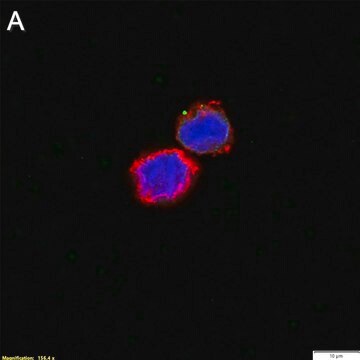
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: Representative lots immunolocalized nuclear R loops by fluorescent immunocytochemistry staining of methanol-fixed H1 human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and formaldehyde-fixed HeLa cells (Bhatia, V., et al. (2014). Nature. 511(7509):362-365; Ginno, P.A., et al. (2012). Mol. Cell. 45(6):814-825).
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipitated in vitro transcribed R-loop substrate (DNA-RNA hybrid), but not doouble-stranded DNA (dsDNA) (Ginno, P.A., et al. (2012). Mol. Cell. 45(6):814-825).
Epigenetics & Nuclear Function
Jakość
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A 1:50 dilution of this antibody immunolocalized nuclear and mitochondrial DNA-RNA hybrids in 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed, 0.3% Triton X-100-permeabilized HeLa cells.
Postać fizyczna
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Inne uwagi
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
polecane
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Przeciwciała łączą się z określonymi antygenami w celu wytworzenia ekskluzywnego kompleksu przeciwciało-antygen. Dowiedz się więcej o naturze tego wiązania i jego wykorzystaniu jako znacznika molekularnego w badaniach.
Poznaj różnice między przeciwciałami monoklonalnymi i poliklonalnymi, w tym sposób generowania przeciwciał, numery klonów i formaty przeciwciał.
Immunofluorescencja wykorzystuje cząsteczki fluorescencyjne sprzężone z przeciwciałami do lokalizacji białek, potwierdzania modyfikacji i wizualizacji kompleksów białkowych.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej