MAB5364
Anti-Reelin Antibody, a.a. 164-496 mreelin, clone G10
clone G10, Chemicon®, from mouse
Synonim(y):
Anti-ETL7, Anti-LIS2, Anti-PRO1598, Anti-RL
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
mouse
Poziom jakości
forma przeciwciała
purified antibody
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
G10, monoclonal
reaktywność gatunkowa
rodent, mouse, rat
reaktywność gatunkowa (przewidywana na podstawie homologii)
human
producent / nazwa handlowa
Chemicon®
metody
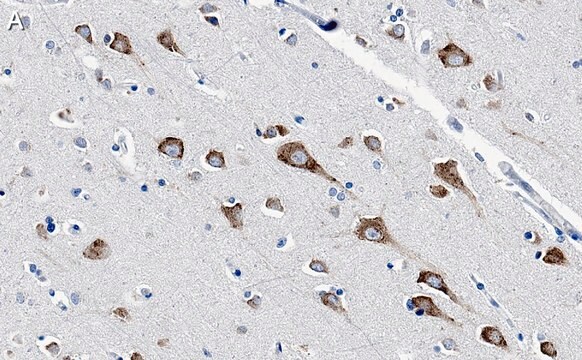
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
izotyp
IgG1
numer dostępu NCBI
numer dostępu UniProt
Warunki transportu
wet ice
docelowa modyfikacja potranslacyjna
unmodified
informacje o genach
human ... RELN(5649)
Opis ogólny
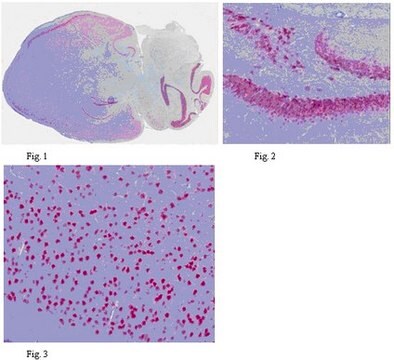
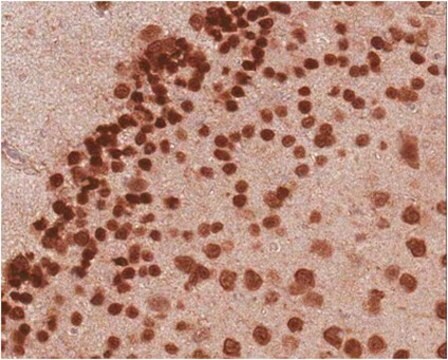
The reeler mutant in mouse displays an abnormal pattern of cell migration throughout the cerebral and cerebellar cortices. The preplate forms normally, and the neurons differentiate at the correct times in the ventricular zone. However, instead of forming the normal "inside-out" arrangement of neurons in the cortical plate, the older neurons are found furthest from the ventricular zone, while the younger neurons do not migrate far at all. The reeler cerebral cortex is inverted from that of the wild type mouse.
The defect of the reeler mice appears to be in the production of an extracellular matrix protein by the Cajal-Retzius cells (D′Arcangelo et al., 1995, Nature 374:719-723.; Ogawa et al., 1995 Neuron 14:899-912.) This 388kDa protein is made by wild-type mice but not by the reeler mutants. It is thought that this Reelin protein is crucial for positioning the migrating neuron within the cortical plate (Figure 1). In the absence of Reelin, the migrating neuron would be "lost," and the cortical plate would be abnormal. We do not yet know the mechanisms by which Reelin informs the cells as to their position, how the cell responds to Reelin, and why the absence of reelin should give an "inverted" plate. However, the identification of the protein encoded by the reeler gene should allow us to begin these studies.
Specyficzność
Immunogen
Zastosowanie
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by the end user.
Neuroscience
Growth Cones & Axon Guidance
Jakość
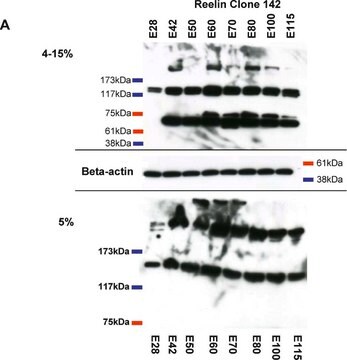
Western Blotting Analysis:
1:500 dilution of this antibody detected reelin on 10 μg of Rat brain lysates.
Opis wartości docelowych
Postać fizyczna
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Komentarz do analizy
Mouse liver, kidney, rat brain lysate
Inne uwagi
Informacje prawne
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Nie możesz znaleźć właściwego produktu?
Wypróbuj nasz Narzędzie selektora produktów.
polecane
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej