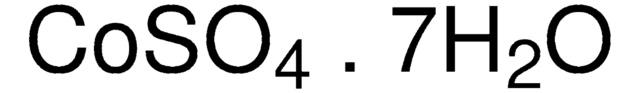Kluczowe dokumenty
939331
Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate

≥99.99% trace metals basis
Synonim(y):
Nickelous Sulfate, Hexahydrate, Battery grade nickel sulfate, Nickel monosulfate hexahydrate, Nickel sulphate hexahydrate
About This Item
Polecane produkty
typ
(High purity Salts)
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥99.99% trace metals basis
98-102% (EDTA, complexometric)
Formularz
powder or crystals
zanieczyszczenia
≤1000 ppm trace metals basis
kolor
faint blue to dark blue-green
pH
4.3-4.7 (20 °C, 100 g/L in water)
rozpuszczalność
water: soluble
gęstość
2.07 g/cm3 at 20 °C
ślady anionów
chloride (Cl-): ≤20 ppm
ślady kationów
Al: <50 ppm
Ca: <50 ppm
Co: <50 ppm
Cu: <50 ppm
Fe: <50 ppm
K: <50 ppm
Mg: <50 ppm
Na: <50 ppm
Pb: <50 ppm
Zn: <50 ppm
InChI
1S/Ni.H2O4S.6H2O/c;1-5(2,3)4;;;;;;/h;(H2,1,2,3,4);6*1H2/q+2;;;;;;;/p-2
Klucz InChI
RRIWRJBSCGCBID-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Therefore, Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate has been widely used as a key component for the synthesis of Cathode for Lithium-ion batteries. - Spherical NCM 622 and Li[Ni0.9Co0.05Mn0.05]O2 (NCM 900505) were synthesized via a co-precipitation method using Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate. In order to achieve the desired energy density, it is necessary to maximize both the nickel content in the cathode and the cutoff voltage. [] - to synthesis single-crystal, Ni-rich NCM and polycrystalline NCM cathodes with various Ni content by coprecipitation method . These Ni-rich layered cathodes like NCM, NCA, and NCMA ([Ni1–x–yCox(Mn and/or Al)y]O2) are the top choices for powering upcoming electric vehicles. It is found that polycrystalline NCM cathodes are prone to intergranular microcracking during cycling, single crystal NCM cathodes demonstrate resilience against mechanical fracture, even under highly charged conditions or repeated cycles. Due to limited lithium-ion diffusion pathways, the electrochemical performance of single crystal -NCM cathodes, particularly in terms of capacity and cycling stability, is lower compared to that of polycrystalline-NCM cathodes. The difference in the electrochemical performance of single crystal -NCM and polycrystalline-NCM cathodes grows as the Ni fraction increases. In addition, Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate is widely used for electroplating for producing metallic coatings. Nickel(II) sulfate hexahydrate can also be used as a catalyst in: -Pt50Ni50 catalysts supported on MCM-41 were produced using wet co-impregnation. These catalysts were then employed for hydrogenation reactions of benzene in gas phase. The morphology of the metal phase within the catalysts has a notable impact on the conversion of benzene to cyclohexane. Factors like reduction temperature, NaBH4 concentration, and reduction medium influence the particle morphology. []
Cechy i korzyści
- Water soluble
- Medium purity (99.9%)
- Low trace metals in ppm level
- Cost effective Suitable for battery applications
- Recycled catalyst
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Carc. 1A Inhalation - Muta. 2 - Repr. 1B - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Organy docelowe
Respiratory Tract
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Przepraszamy, ale COA dla tego produktu nie jest aktualnie dostępny online.
Proszę o kontakt, jeśli potrzebna jest pomoc Obsługa Klienta
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej