Kluczowe dokumenty
764752
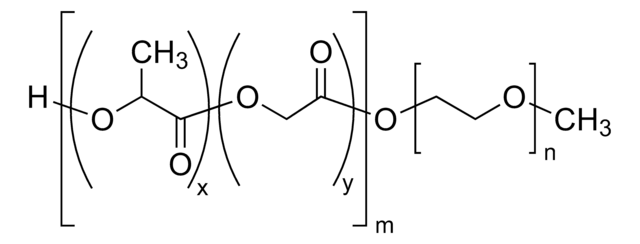
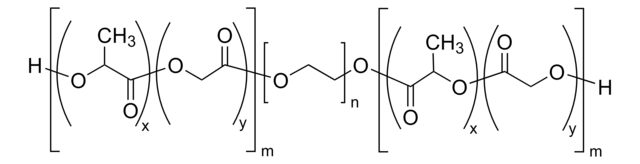
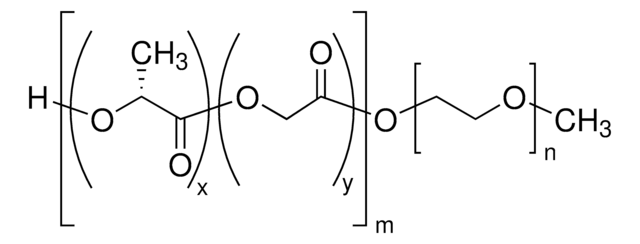
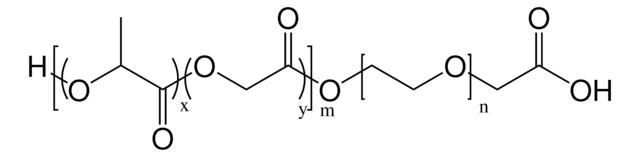
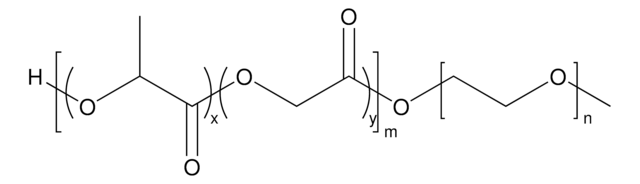
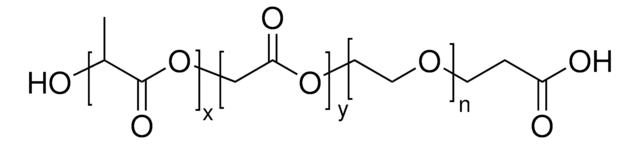
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-block-poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
PEG average Mn 5,000, PLGA Mn 55,000
Synonim(y):
PEG-PLGA, Polyethylene glycol, mPEG-b-PLGA, mPEG-b-PLGA
About This Item
Polecane produkty
opis
typical PEG PDI < 1.1; overall PDI < 2.5
Poziom jakości
Postać
pellets
proporcje
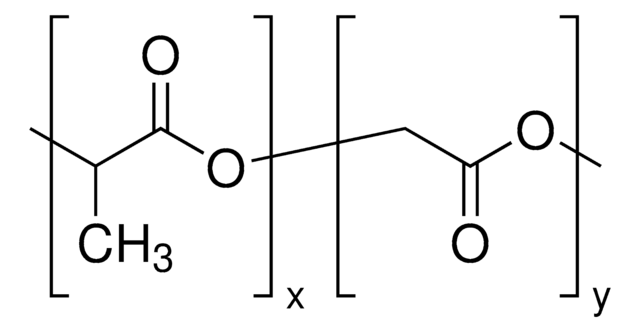
lactide:glycolide 50:50
masa cząsteczkowa
PEG average Mn 5,000
PLGA Mn 55,000
average Mn 60,000 (total)
ramy czasowe degradacji
1-4 weeks
temp. przejścia
Tg 10 °C(lit.)
Tm 254-259 °C
PDI
<1.2
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Cechy i korzyści
- Good biocompatibility, low immunogenicity and good degradability.
- Properties can be easily modulated by changing the block copolymer segment sizes to suit a particular application.
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
One of the common difficulties with intravenous drug delivery is low solubility of the drug. The requirement for large quantities of saline to dissolve such materials limits their clinical use, and one solution for this problem that has recently generated interest is the formation of drug-loaded micelles.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
Microparticle drug delivery systems have been extensively researched and applied to a wide variety of pharmaceutical and medical applications due to a number of advantages including injectability, local applicability to target tissues and sites, and controlled drug delivery over a given time period.
Opracowanie leków ukierunkowanych na określone miejsca w ludzkim ciele pozostaje obecnie jednym z największych wyzwań w biomedycynie.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej