Key Documents
274135
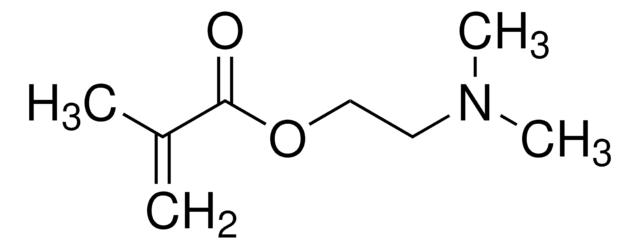
N,N-Dimethylacrylamide
99%, contains 500 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Synonim(y):
2-Propenamide
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
99%
Postać
liquid
zawiera
500 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
współczynnik refrakcji
n20/D 1.473 (lit.)
tw
80-81 °C/20 mmHg (lit.)
gęstość
0.962 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
CN(C)C(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C5H9NO/c1-4-5(7)6(2)3/h4H,1H2,2-3H3
Klucz InChI
YLGYACDQVQQZSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- Synthesis of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMAA) nanoparticles which are used in biomedical and drug delivery applications.
- Use as a co-monomer in the synthesis of thermoresponsive polymers used in smart coatings, adhesives, and sensors.
- As a reactive diluent in the manufacture of UV-cured coatings and inks.
- Use as a co-monomer with polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA) and a chitosan derivative to develop an injectable hydrogel that can be used as a bone tissue engineering matrix.
- A series of DMMA-based hydrogels for the removal of heavy metals and organic dyes from polluted water. These hydrogels are highly efficient in removing cationic dyes due to electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding in the DMMA backbone.
- Non-toxic luminescent carbon dot/poly(DMMA) nanocomposite via surface-initiated reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization.
- Polymer coating for quartz crystal microbalance(QCM) sensor. The poly(DMMA) gel acts as a sensing material to adsorb Au(III) ions from HCl aqueous solution and it is inactive to most other metal ions and organic compounds.
Cechy i korzyści
- It is an appropriate precursor for copolymerization due to its low initiation temperature and high reactivity.
- Its unique structure forms a 3D network and improves the water retention capacity of hydrogels.
- It is highly soluble in water.
- It can easily bind to colloidal particles to enhance the bridging effect which plays a key role in flocculation.
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
158.0 °F
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
70 °C
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej



![N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]methacrylamide 99%, contains MEHQ as inhibitor](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/295/145/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951/640/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951.png)
![3-[Tris(trimethylsiloxy)silyl]propyl methacrylate contains MEHQ + HQ as stabilizer, 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/148/664/33ff5116-f264-4a64-824a-009c2ca5b2b3/640/33ff5116-f264-4a64-824a-009c2ca5b2b3.png)