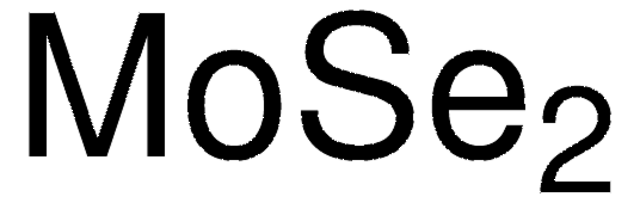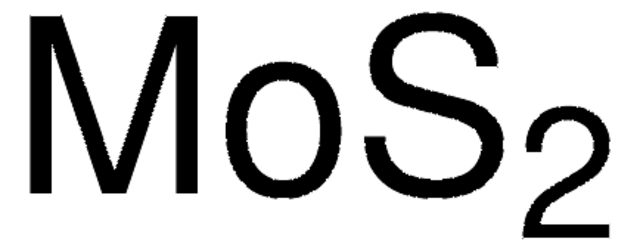Key Documents
234842
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide
powder, <2 μm, 98%
Synonim(y):
Molybdenum disulfide
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
98%
Postać
powder
charakterystyka ekologicznej alternatywy
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
wielkość cząstki
<2 μm
gęstość
5.06 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Zastosowanie
battery manufacturing
kategoria ekologicznej alternatywy
, Enabling
ciąg SMILES
S=[Mo]=S
InChI
1S/Mo.2S
Klucz InChI
CWQXQMHSOZUFJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Opakowanie
Kod klasy składowania
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
nwg
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Developed in the last several years, fluorescence quenching microscopy (FQM) has enabled rapid, inexpensive, and high-fidelity visualization of two-dimensional (2D) materials such as graphene-based sheets and MoS2.
Nanostructured Materials Through Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
The production of hydrogen by catalytic water splitting is important for a wide range of industries including renewable energy petroleum refining and for the production of methanol and ammonia in the chemical industry.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej