おすすめの製品
品質水準
アッセイ
≥98% (HPLC)
フォーム
powder
色
white to beige
溶解性
DMSO: ≥10 mg/mL, clear
保管温度
−20°C
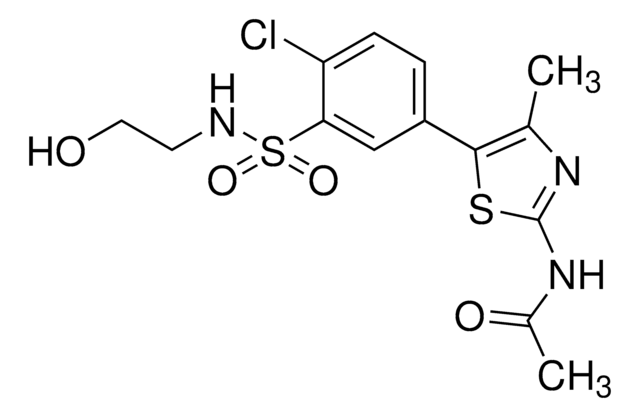
SMILES記法
CS(C(C=C1)=CC=C1C2=NC(C(NC3=CC=CC=C3)=O)=C(N)N=C2)(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C18H16N4O3S/c1-26(24,25)14-9-7-12(8-10-14)15-11-20-17(19)16(22-15)18(23)21-13-5-3-2-4-6-13/h2-11H,1H3,(H2,19,20)(H,21,23)
InChI Key
DUIHHZKTCSNTGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
アプリケーション
VE-821は、ヒト癌細胞のATMおよびRad3関連(ATR)タンパク質の阻害剤として使用されます。
生物化学的/生理学的作用
VE-821は、DNA損傷応答(DDR)キナーゼである、毛細血管拡張性運動失調症遺伝子(ATM)、並びにATMおよびRad3関連遺伝子(ATR)の強力なATP競合阻害剤であり、Kiは13 nMです。VE-821は、関連するPIKK ATM、DNA依存性プロテインキナーゼ(DNA-PK)、mTORおよびPI3-kinase-γに対して(Ki 値は、それぞれ16 μM、2.2 μM、> 1 μMおよび3.9 μM)、そして、無関係の大部分のプロテインキナーゼに対して、最小限の交差反応性を示します。VE-821を単独で使用すると、癌細胞集団の大部分で細胞死を引き起こし、遺伝毒性物質との強い相乗効果も示します。 VE-821は、放射線に対する細胞の感受性を高め、さまざまな化学療法剤に対して癌細胞を感作します。
その他情報
VE-821は、Chemical Probes Portalで専門家によるレビューおよび推奨を受けています。詳細については、Chemical Probes PortalのWebサイトのVE-821プローブの概要をご覧ください 。
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
SML1415-VAR:
SML1415-5MG:
SML1415-25MG:
SML1415-BULK:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Anastazja Poczta et al.
Scientific reports, 9(1), 14135-14135 (2019-10-03)
The present study investigated the effect of cladribine (CLA) and six of its derivatives containing a formamidine group at position 6 (CLA-FDM, CLA-FPAZ, CLA-FPIR, CLA-FPIP, CLA-FHEX, and CLA-FMOR) on acute promyelocytic, lymphoblastic, and acute monocytic leukemia cells. The role of
Human cancer cells utilize mitotic DNA synthesis to resist replication stress at telomeres regardless of their telomere maintenance mechanism
Ozgun Ozer, et al.
Oncotarget null
Tingting Li et al.
Aging, 12(14), 14791-14807 (2020-07-21)
Protection of telomere 1 (POT1), the telomeric single-stranded DNA (ssDNA)-binding protein in the shelterin complex, has been implicated in the DNA damage response, tumorigenesis and aging. Telomere dysfunction induced by telomere deprotection could accelerate cellular senescence in primary human cells.
Aaron Mendez-Bermudez et al.
Molecular cell, 70(3), 449-461 (2018-05-05)
Hard-to-replicate regions of chromosomes (e.g., pericentromeres, centromeres, and telomeres) impede replication fork progression, eventually leading, in the event of replication stress, to chromosome fragility, aging, and cancer. Our knowledge of the mechanisms controlling the stability of these regions is essentially
Camelia Mocanu et al.
Cell reports, 39(3), 110701-110701 (2022-04-21)
Mitotic DNA synthesis (MiDAS) has been proposed to restart DNA synthesis during mitosis because of replication fork stalling in late interphase caused by mild replication stress (RS). Contrary to this proposal, we find that cells exposed to mild RS in
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)