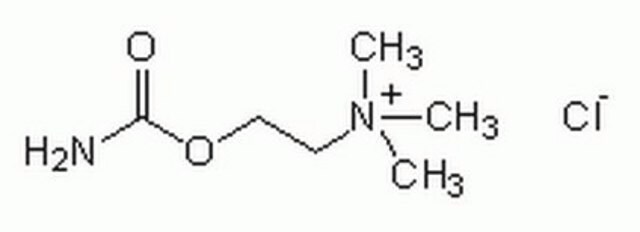
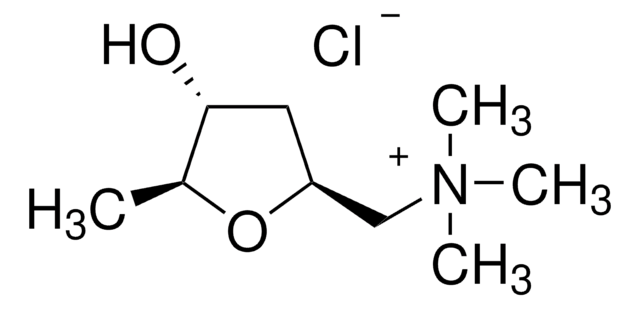
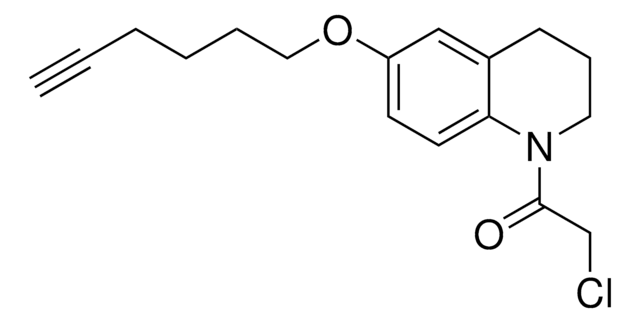
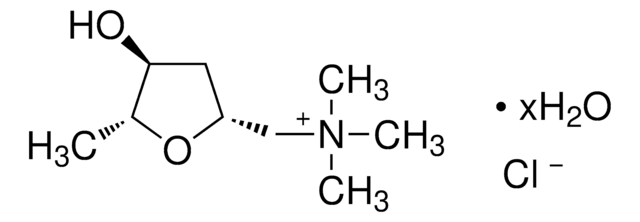
おすすめの製品
フォーム
solid
色
white
溶解性
H2O: 24 mg/mL
ethanol: 4.6 mg/mL
保管温度
2-8°C
SMILES記法
[I-].C[N+](C)(C)CC#CCN1CCCC1=O
InChI
1S/C11H19N2O.HI/c1-13(2,3)10-5-4-8-12-9-6-7-11(12)14;/h6-10H2,1-3H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
InChI Key
VVLMSCJCXMBGDI-UHFFFAOYSA-M
遺伝子情報
human ... CHRM1(1128) , CHRM2(1129) , CHRM3(1131) , CHRM4(1132) , CHRM5(1133)
アプリケーション
- Caenorhabditis elegans(線虫)の運動に対する急性作用を検討するため
- 線維芽細胞成長因子受容体1(FGFR1)のリン酸化を検討するために海馬ニューロンを処理するため
- ラットにおいて膀胱過活動を誘発させるため
生物化学的/生理学的作用
特徴および利点
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Acute Tox. 1 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 2 Dermal - Acute Tox. 2 Oral
保管分類コード
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
労働安全衛生法名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
労働安全衛生法名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
Jan Code
O100-VAR:
O100-100MG:4548173996738
O100-500MG:4548173996745
O100-BULK:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)