おすすめの製品
アプリケーション
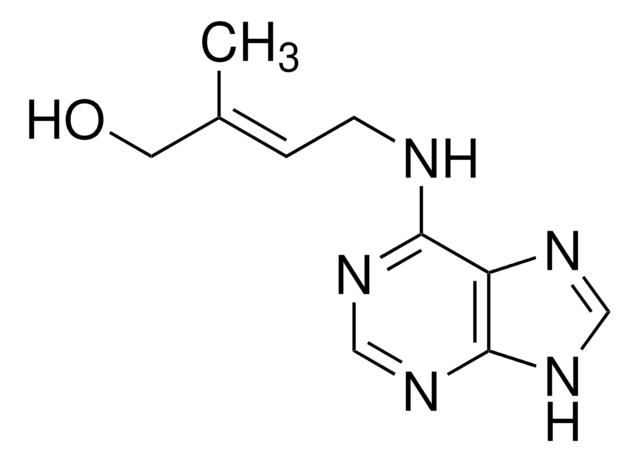
インドール-3-酪酸(IBA)は、オーキシンファミリーの植物ホルモンです。IBAは、植物において自然に発生・機能する最も豊富で基本的なオーキシンである、インドール-3-酢酸(IAA)の前駆体と考えられています。IAAは、インタクトな植物におけるオーキシン作用の大部分を生じる、最も強力な天然オーキシンです。
調製ノート
関連製品
製品番号
詳細
価格
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
保管分類コード
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
労働安全衛生法名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
労働安全衛生法名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
Jan Code
I5386-25G:
I5386-VAR:
I5386-1G:
I5386-BULK:
I5386-100MG:
I5386-5G:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Lucia C Strader et al.
Plant physiology, 153(4), 1577-1586 (2010-06-22)
Genetic evidence in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) suggests that the auxin precursor indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) is converted into active indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) by peroxisomal beta-oxidation; however, direct evidence that Arabidopsis converts IBA to IAA is lacking, and the role of IBA-derived
Shengbin Liu et al.
Plant physiology (2021-10-19)
In cultivated grasses, tillering, leaf, and inflorescence architecture, as well as abscission ability, are major agronomical traits. In barley (Hordeum vulgare), maize (Zea mays), rice (Oryza sativa), and brachypodium (Brachypodium distachyon), NOOT-BOP-COCH-LIKE (NBCL) genes are essential regulators of vegetative and
Kamil Ruzicka et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(23), 10749-10753 (2010-05-26)
Differential distribution of the plant hormone auxin within tissues mediates a variety of developmental processes. Cellular auxin levels are determined by metabolic processes including synthesis, degradation, and (de)conjugation, as well as by auxin transport across the plasma membrane. Whereas transport
Fatima Naim et al.
PloS one, 15(1), e0227994-e0227994 (2020-01-25)
Introducing a new trait into a crop through conventional breeding commonly takes decades, but recently developed genome sequence modification technology has the potential to accelerate this process. One of these new breeding technologies relies on an RNA-directed DNA nuclease (CRISPR/Cas9)
Lucia C Strader et al.
The Plant cell, 23(3), 984-999 (2011-03-17)
Levels of auxin, which regulates both cell division and cell elongation in plant development, are controlled by synthesis, inactivation, transport, and the use of storage forms. However, the specific contributions of various inputs to the active auxin pool are not
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)