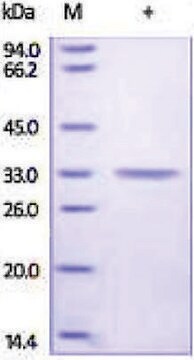
おすすめの製品
アプリケーション
ヒトの炭酸脱水酵素IIは、虚血/再灌流のin vitroモデルにおけるミトコンドリアおよびサイトゾルの遊離亜鉛レベルの定量的イメージングを評価する研究で使用されています。ヒト炭酸脱水酵素IIは、触媒的にCO2を水和するための新しいスクラバーの概念を調査する研究でも使用されています。
生物化学的/生理学的作用
炭酸脱水酵素は、二酸化炭素の炭酸への水和を触媒する亜鉛金属酵素です。pHやCO2の恒常性、重炭酸塩とCO2の輸送、生合成反応、骨吸収、石灰化、腫瘍形成など生命維持に重要となる生理学的および病理学的プロセスに関与しています。腎酸性化に必要です。炭酸脱水酵素が欠乏すると、骨粗鬆症、尿細管性アシドーシス、および脳内石灰化を引き起こすおそれがあります。したがって、この酵素は、緑内障、てんかん、パーキンソン病の臨床に応用できる阻害剤の重要な標的です。さらに、肥満とがんの潜在的な標的としても探索されています。CAIIの分子量は約30 kDaで、主にII型肺細胞に存在します。このような場所に局在化していることから、CAIIは体液分泌の調節やCO2排出の亢進などの肺機能に関与していると推測されています。スルホンアミド、スルファメートおよびスルファミドは、CAの強力な阻害剤です。
単位の定義
1 Wilbur-Anderson(W-A) unitは、0°C、1分間に、0.02 MトリズマバッファーのpHを8.3から6.3に低下させる酵素量です(1 W-A unitは、Roughton-Booth unitと実質的に等価です)。
物理的形状
20 mM Tris(pH 7.5)、150 mM NaClで調製した溶液。
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
C6624-BULK:
C6624-VAR:
C6624-500UG-PW:
C6624-500UG:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Samira Ranjbar et al.
International journal of biological macromolecules, 50(4), 910-917 (2012-02-22)
This study reports the interaction between furosemide and human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) using fluorescence, UV-vis and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Fluorescence data indicated that furosemide quenches the intrinsic fluorescence of the enzyme via a static mechanism and hydrogen
Bryan J McCranor et al.
Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes, 44(2), 253-263 (2012-03-21)
The role of zinc ion in cytotoxicity following ischemic stroke, prolonged status epilepticus, and traumatic brain injury remains controversial, but likely is the result of mitochondrial dysfunction. We describe an excitation ratiometric fluorescence biosensor based on human carbonic anhydrase II
New scrubber concept for catalytic CO2 hydration by immobilized carbonic anhydrase II and in-situ inhibitor removal in three-phase monolith slurry reactor
Iliuta, I. and F. Larachi
Separation and Purification Technology, 86, 199-214 (2012)
John J Desmarais et al.
Nature microbiology, 4(12), 2204-2215 (2019-08-14)
Bacterial autotrophs often rely on CO2 concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) to assimilate carbon. Although many CCM proteins have been identified, a systematic screen of the components of CCMs is lacking. Here, we performed a genome-wide barcoded transposon screen to identify essential
Screening and docking studies of natural phenolic inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase II
Huang HQ, et al.
Science in China. Series B, Chemistry, Life Sciences & Earth Sciences, 52(3), 332-337 (2009)
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)