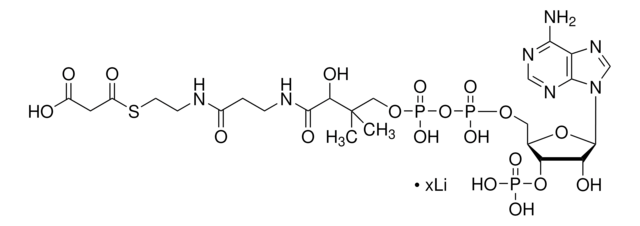
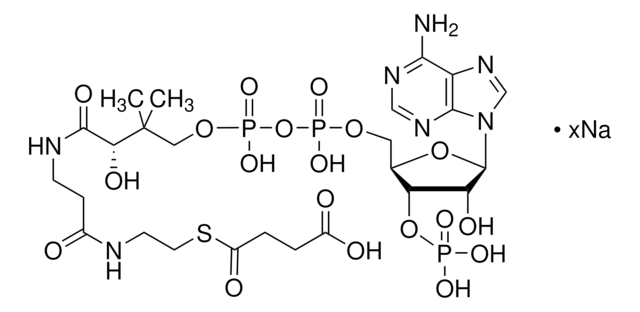
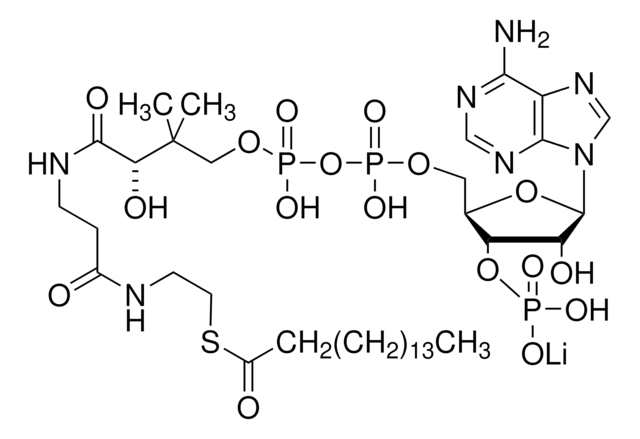
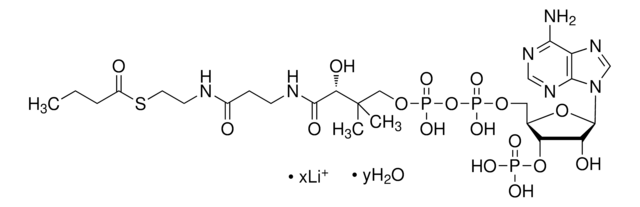
About This Item
おすすめの製品
品質水準
アッセイ
≥93% (HPLC)
形状
powder
溶解性
H2O: 100 mg/mL
保管温度
−20°C
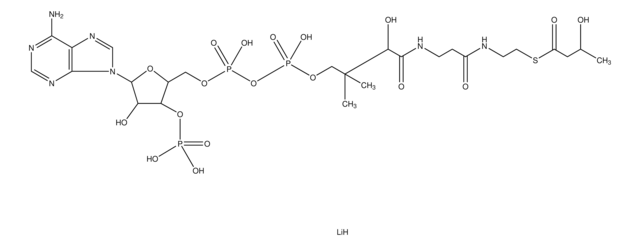
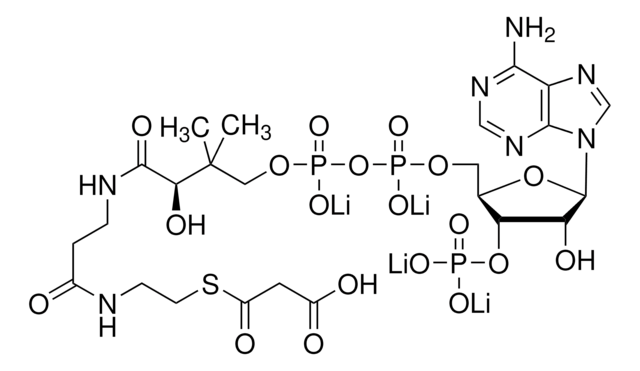
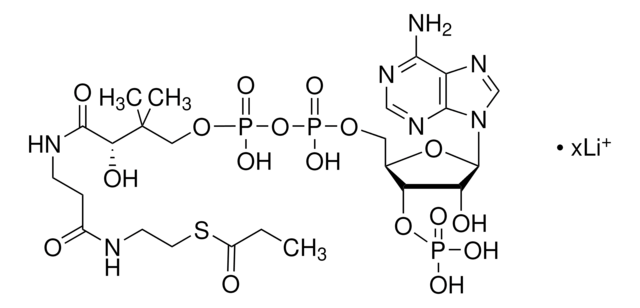
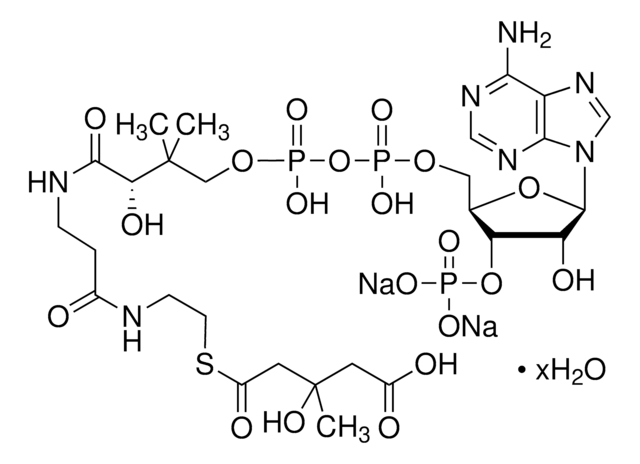
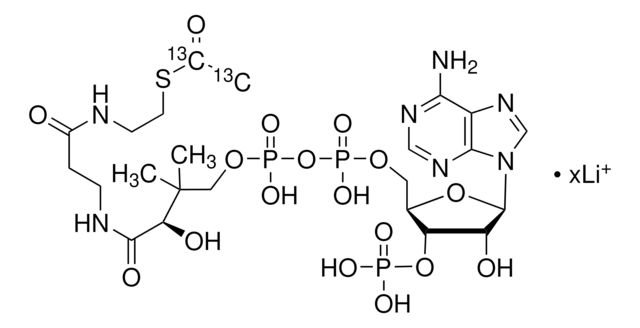
SMILES記法
O[C@H]1[C@](O[C@@H]([C@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)COP(OP(OCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(NCCC(NCCSC(C)=O)=O)=O)(O)=O)(O)=O)([H])N2C3=NC=NC(N)=C3N=C2.[3Na]
InChI
1S/C23H38N7O17P3S.Na/c1-12(31)51-7-6-25-14(32)4-5-26-21(35)18(34)23(2,3)9-44-50(41,42)47-49(39,40)43-8-13-17(46-48(36,37)38)16(33)22(45-13)30-11-29-15-19(24)27-10-28-20(15)30;/h10-11,13,16-18,22,33-34H,4-9H2,1-3H3,(H,25,32)(H,26,35)(H,39,40)(H,41,42)(H2,24,27,28)(H2,36,37,38);/q;+1/p-1/t13-,16-,17-,18?,22-;/m1./s1
InChI Key
HNLIOWFIXSPFEC-WLYMNMRISA-M
遺伝子情報
human ... CHAT(1103) , HAT1(8520) , KAT2A(2648) , KAT2B(8850) , KAT5(10524)
mouse ... HAT1(107435) , KAT2A(14534) , KAT2B(18519) , KAT5(81601)
rat ... HAT1(296501) , KAT2A(303539) , KAT2B(301164) , KAT5(192218)
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
アプリケーション
生物化学的/生理学的作用
調製ノート
その他情報
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
A2056-10MG:4548174006108
A2056-1MG:4548174006115
A2056-PM:
A2056-BULK:
A2056-5MG:4548174006139
A2056-25MG:4548174006122
A2056-VAR:
A2056-100MG:4548174006092
A2056-10MG-KC:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
資料
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about how proliferatively active cells require both a source of carbon and of nitrogen for the synthesis of macromolecules. Although a large proportion of tumor cells utilize aerobic glycolysis and shunt metabolites away from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, many tumor cells exhibit increased mitochondrial activity.
Get to know the Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to better inform your research in biochemistry, metabolomics, or related fields concerned with this metabolic pathway and its enzymes, by-products, or intermediates.
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)