おすすめの製品
品質水準
アッセイ
≥97%
形状
powder or crystals
反応適合性
reagent type: catalyst
reaction type: Photocatalysis
mp
171 °C
光触媒活性化
400 nm
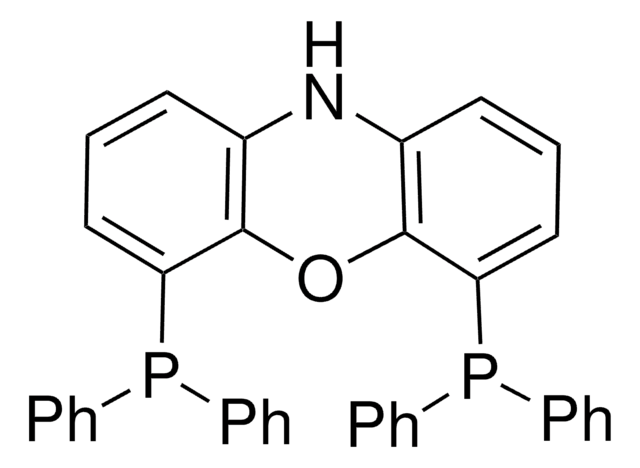
SMILES記法
C1(C=CC(C2=CC=C(C3=CC=CC=C3)C=C2)=C4)=C4OC(C=C(C5=CC=C(C6=CC=CC=C6)C=C5)C=C7)=C7N1C8=C(C=CC=C9)C9=CC=C8
アプリケーション
このフェノキサジン系の有機光酸化還元触媒(ジヒドロフェナジン触媒901112に加え)は強力な励起状態還元剤として設計され、優れた光物理的特性および電気化学的特性を有しており、こうした特性によりルテニウムまたはイリジウム系光酸化還元触媒の持続可能な代替となっています。例えば、ジヒドロフェナジンおよびフェノキサジン誘導体は、制御されたポリマー合成、ならびにトリフルオロメチル化、原子移動ラジカル付加、およびニッケル/光酸化還元二重触媒によるC-NおよびC-Sクロスカップリングなどの小分子転移のための、光酸化還元触媒型原子移動ラジカル重合(ATRP)の用途において、ルテニウムまたはイリジウム錯体の代替となることが示されました。ジヒドロフェナジンおよびフェノキサジン系の有機光酸化還元触媒は、Miyake Research Groupとの共同研究で紹介されました。
本製品はメルクの一連のフォトリアクター:Penn PhD(Z744035)& SynLED 2.0(Z744080)などと共に使用できます。
本製品はメルクの一連のフォトリアクター:Penn PhD(Z744035)& SynLED 2.0(Z744080)などと共に使用できます。
その他情報
法的情報
特許出願PCT/US2016/058245。New Iridium社と共同販売。25 gを超えるご注文の場合、New Iridium(https://www.newiridium.com)にてご確認、または、担当者(chern@newiridium.com)までお問い合わせください。
Phenox O-PC is a trademark of New Iridium LLC
関連製品
製品番号
詳細
価格
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
901111-1G:
901111-100MG:
901111-VAR:
901111-BULK:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
Organocatalyzed Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization Using N-Aryl Phenoxazines as Photoredox Catalysts.
Pearson, et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 138, 11399-11407 (2017)
Jordan C Theriot et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 352(6289), 1082-1086 (2016-04-02)
Atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) has become one of the most implemented methods for polymer synthesis, owing to impressive control over polymer composition and associated properties. However, contamination of the polymer by the metal catalyst remains a major limitation. Organic
Ya Du et al.
Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 23(46), 10962-10968 (2017-06-28)
Photoredox catalysis is a versatile approach for the construction of challenging covalent bonds under mild reaction conditions, commonly using photoredox catalysts (PCs) derived from precious metals. As such, there is need to develop organic analogues as sustainable replacements. Although several
Ryan M Pearson et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 138(35), 11399-11407 (2016-08-25)
N-Aryl phenoxazines have been synthesized and introduced as strongly reducing metal-free photoredox catalysts in organocatalyzed atom transfer radical polymerization for the synthesis of well-defined polymers. Experiments confirmed quantum chemical predictions that, like their dihydrophenazine analogs, the photoexcited states of phenoxazine
Chern-Hooi Lim et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 139(1), 348-355 (2016-12-16)
Photoexcited intramolecular charge transfer (CT) states in N,N-diaryl dihydrophenazine photoredox catalysts are accessed through catalyst design and investigated through combined experimental studies and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. These CT states are reminiscent of the metal to ligand charge transfer
資料
Photoredox catalysis is a powerful synthetic methodology to form challenging covalent bonds using light irradiation. It is effective for light-driven polymer and small molecule synthesis.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)


![Ir[dF(CF3)ppy]2(dtbpy))PF6](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/982/913/02dd8ddd-6deb-40a0-ab9b-07b18f1abb09/640/02dd8ddd-6deb-40a0-ab9b-07b18f1abb09.png)





![トリス[2-フェニルピリジナート-C2,N]イリジウム(III) sublimed grade](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/167/234/658d0b76-d31d-4fd5-8041-e04e207227c9/640/658d0b76-d31d-4fd5-8041-e04e207227c9.png)