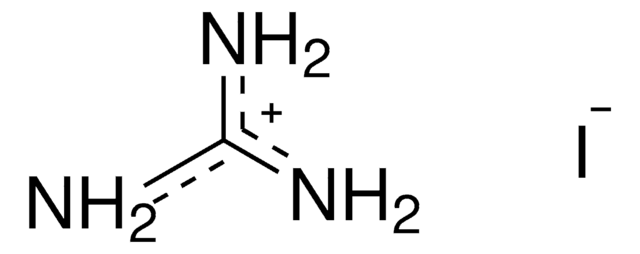
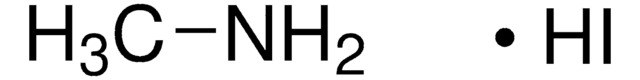おすすめの製品
アッセイ
98%
品質水準
形状
powder
環境により配慮した代替製品の特徴
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
mp
100 °C
環境により配慮した代替製品カテゴリ
SMILES記法
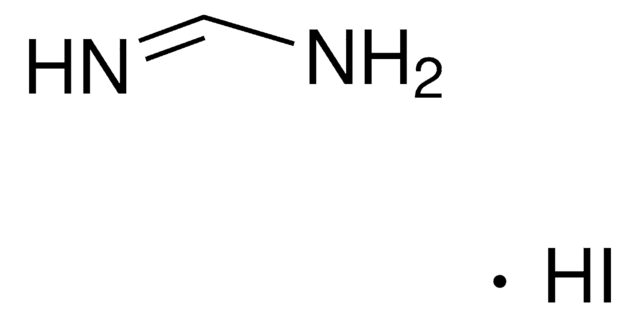
CC(N)=[NH2+].[I-]
InChI
1S/C2H6N2.HI/c1-2(3)4;/h1H3,(H3,3,4);1H
InChI Key
GGYGJCFIYJVWIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
詳細
アプリケーション
法的情報
Greatcell Solar is a registered trademark of Greatcell Solar Materials Pty Ltd.
シグナルワード
Warning
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
ターゲットの組織
Respiratory system
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
労働安全衛生法名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を表示すべき危険物及び有害物
労働安全衛生法名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
名称等を通知すべき危険物及び有害物
Jan Code
805971-BULK:
805971-25G:4548174001417
805971-5G:4548174001424
805971-VAR:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
資料
Next generation solar cells have the potential to achieve conversion efficiencies beyond the Shockley-Queisser (S-Q) limit while also significantly lowering production costs.
Dr. Perini and Professor Correa-Baena discuss the latest research and effort to obtain higher performance and stability of perovskite materials.
For several decades, the need for an environmentally sustainable and commercially viable source of energy has driven extensive research aimed at achieving high efficiency power generation systems that can be manufactured at low cost.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)