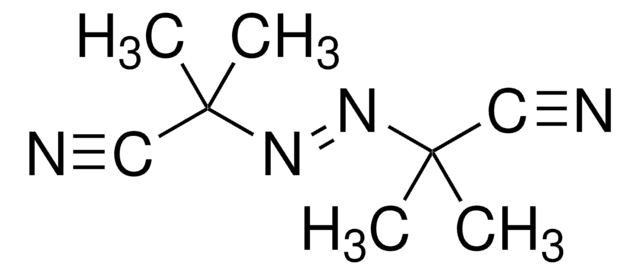
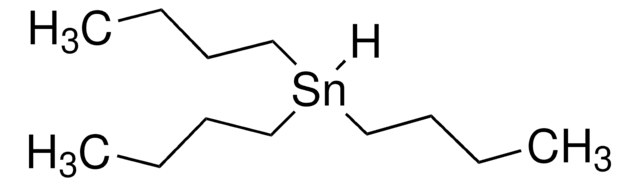
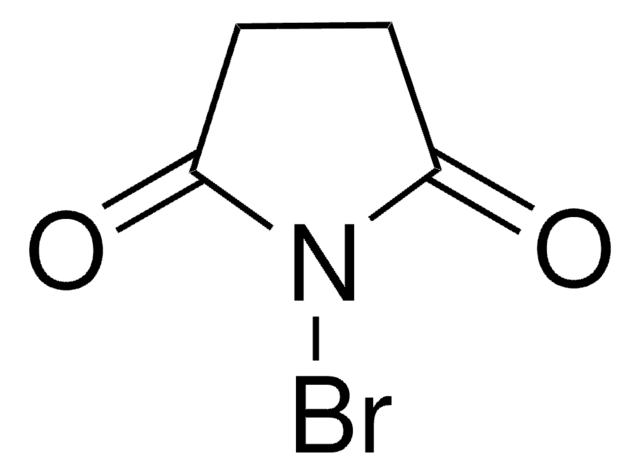
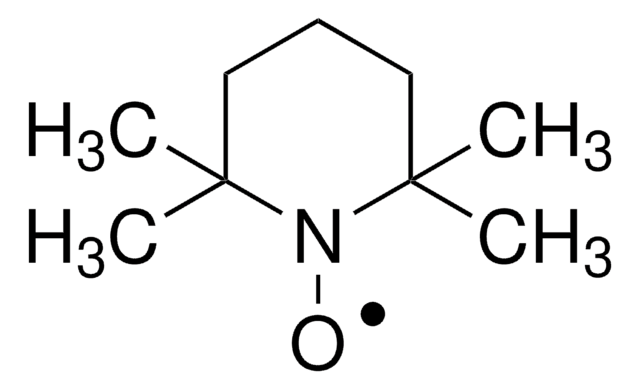
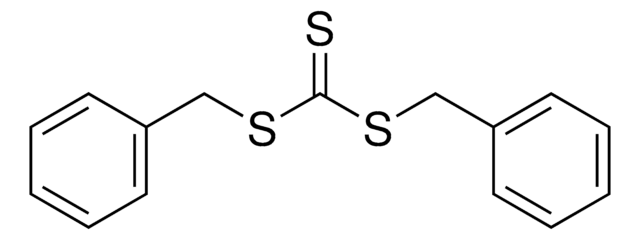
おすすめの製品
詳細
アプリケーション
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Eye Irrit. 2 - Self-react. D - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
ターゲットの組織
Respiratory system
保管分類コード
5.2 - Organic peroxides and self-reacting hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
毒物及び劇物取締法
劇物
消防法
第5類:自己反応性物質
アゾ化合物
危険等級I
第一種自己反応性物質
Jan Code
380210-5KG:
380210-100G:4548173218878
380210-VAR:
380210-10KG:
380210-BULK:
380210-25G:4548173218861
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
資料
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
RAFT (Reversible Addition Fragmentation chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Tools for Performing ATRP
プロトコル
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)