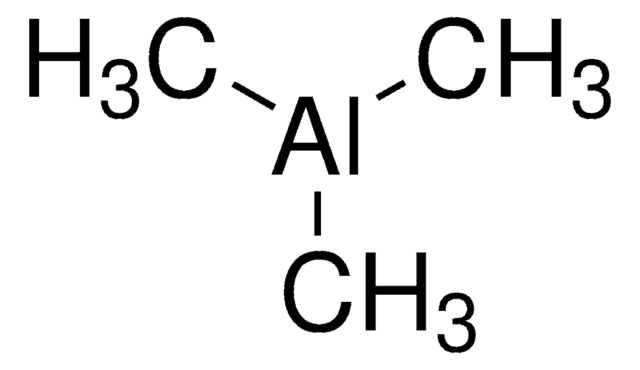
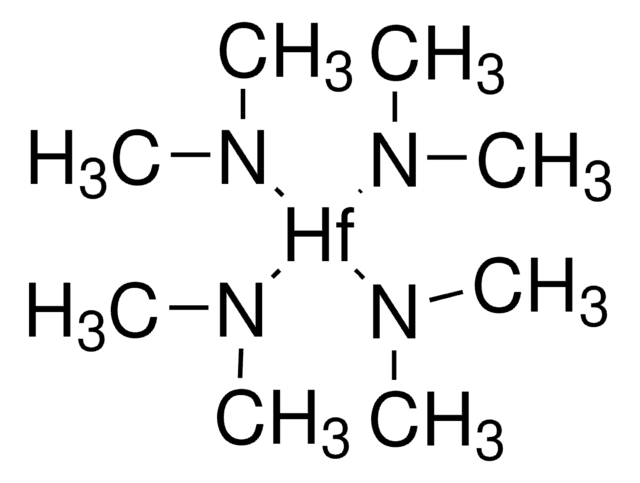
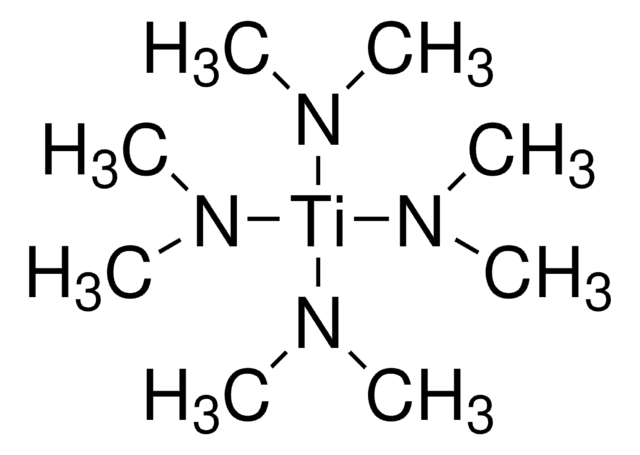
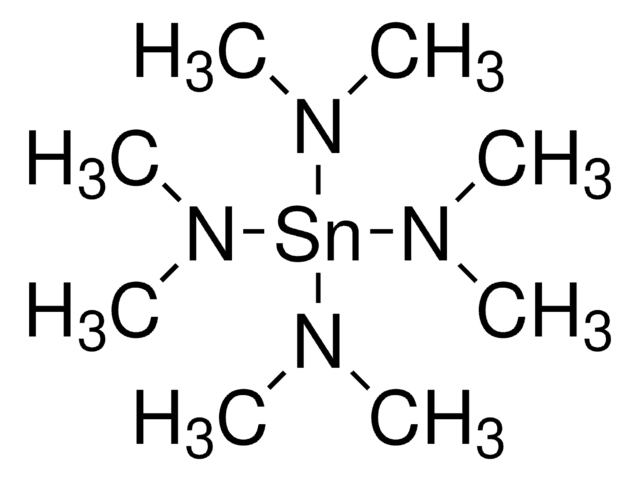
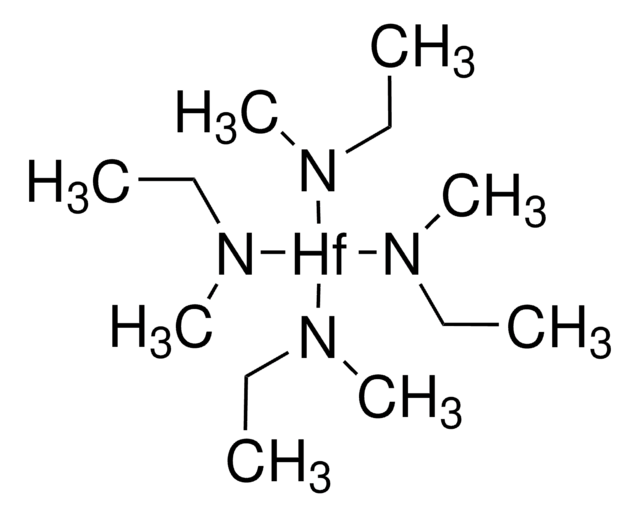
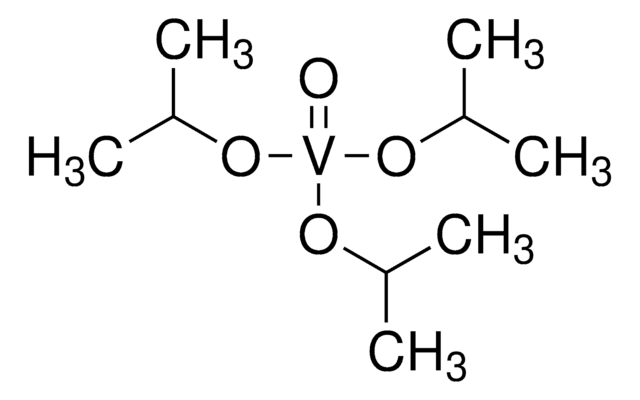
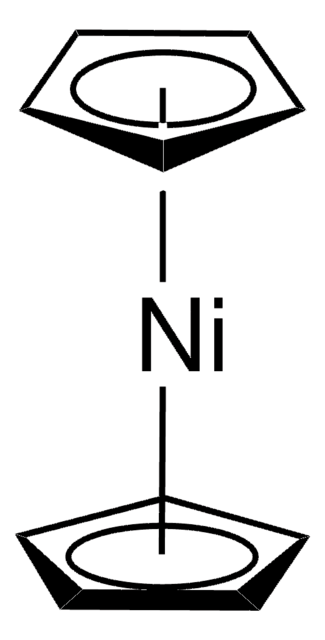
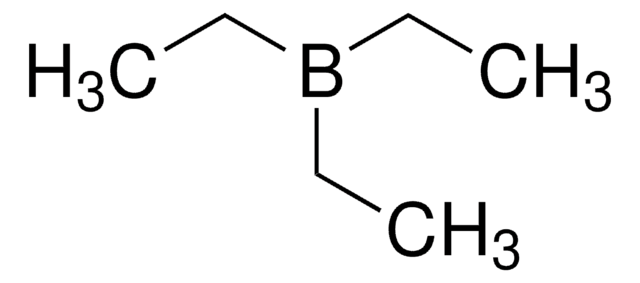
推荐产品
形狀
liquid
折射率
n20/D 1.498 (lit.)
bp
117 °C (lit.)
mp
−28 °C (lit.)
密度
1.205 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES 字串
CC[Zn]CC
InChI
1S/2C2H5.Zn/c2*1-2;/h2*1H2,2H3;
InChI 密鑰
HQWPLXHWEZZGKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
應用
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Pyr. Liq. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - Water-react 1
安全危害
儲存類別代碼
4.2 - Pyrophoric and self-heating hazardous materials
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
其他客户在看
商品
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) techniques have emerged in the last ten years to meet various needs including semiconductor device miniaturization, conformal deposition on porous structures and coating of nanoparticles. ALD is based on two sequential self-limiting surface reactions.
Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) is a coating technology that allows perfectly conformal deposition onto complex 3D surfaces. The reason for this uniform coating lies in the saturative chemisorption of sequential cycles of precursor vapors.
Since the demonstration of the first practical solar cell 60 years ago, research on novel materials, improved solar cell design and structure, and innovative manufacturing processes have all contributed to a continuous increase in the efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) devices.
Nanomaterials are considered a route to the innovations required for large-scale implementation of renewable energy technologies in society to make our life sustainable.
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门