MAK161
Multidrug Resistance Assay Kit
(Fluorometric MDR Assay)
Sinonimo/i:
MDR Assay
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.84
Prodotti consigliati
impiego
(Fluorometric MDR Assay)
applicazioni
pharmaceutical
Metodo di rivelazione
fluorometric
Malattie correlate
cancer
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Informazioni sul gene
human ... ABCB1(5243) , ABCC2(1244)
mouse ... ABCC2(12780)
rat ... abcc2(25303)
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
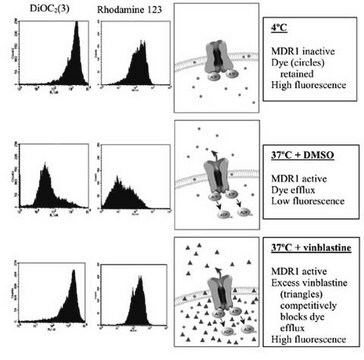
Acquired resistance to chemotherapy drugs, multidrug resistance or MDR, is a major contributor to treatment failure for many types of cancers. MDR is typically associated with the increased expression of two ATP-dependent drug efflux pumps, P-Glycoprotein (P-gp or MDR1) and the Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein (MRP1). These pumps actively expel chemotherapeutic agents, typically hydrophobic amphipathic natural products, from the cytoplasm to exterior of the cell.
This kit is utilizes a hydrophobic fluorescent dye molecule to assess MDR activity in cells. This dye rapidly penetrates cell membranes and becomes trapped resulting in an increase in fluorescence intensity (λex = 490/λem = 525 nm). In cells expressing MDR transporters, the dye is rapidly extruded by the transporters, resulting in decreased fluorescence intensity.
This kit is utilizes a hydrophobic fluorescent dye molecule to assess MDR activity in cells. This dye rapidly penetrates cell membranes and becomes trapped resulting in an increase in fluorescence intensity (λex = 490/λem = 525 nm). In cells expressing MDR transporters, the dye is rapidly extruded by the transporters, resulting in decreased fluorescence intensity.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Compatible with high-throughput handling systems.
Compatibilità
This kit is suitable for the screening of MDR pump inhibitors or for identifying cell lines with high MDR activity.
Principio
This kit is utilizes a hydrophobic fluorescent dye molecule to assess MDR activity in cells. This dye rapidly penetrates cell membranes and becomes trapped resulting in an increase in fluorescence intensity (λEx = 490/λEm = 525 nm). In cells expressing MDR transporters, the dye is rapidly extruded by the transporters, resulting in decreased fluorescence intensity.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Drug resistance in cancer: an overview.
Housman G, et al.
Cancer, 6(3), 1769-1792 (2014)
Non-coding polymorphisms in nucleotide binding domain 1 in ABCC1 gene associate with transcript level and survival of patients with breast cancer.
Kunicka T, et al.
PLoS ONE, 9(7), e101740-e101740 (2014)
Mechanisms and insights into drug resistance in cancer.
Zahreddine H and Katherine B
Frontiers in Pharmacology, 4, 28-28 (2013)
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.