E6412
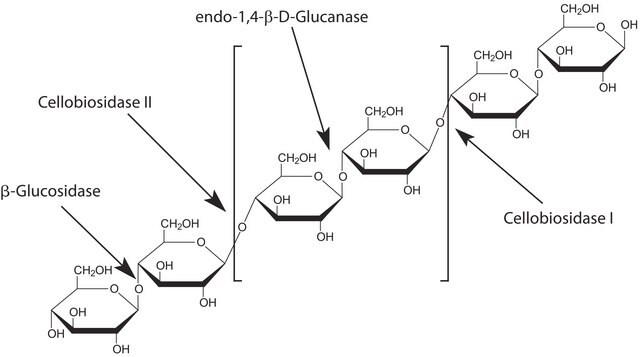
Cellobiohydrolase I from Hypocrea jecorina
0.13 U/mg, recombinant, expressed in corn
Sinonimo/i:
Cel7A, Cellobiosidase, Cellulase
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Ricombinante
expressed in corn
Livello qualitativo
Forma fisica
liquid
Attività specifica
0.13 U/mg
Caratteristiche più verdi
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Categoria alternativa più verde
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Definizione di unità
Stato fisico
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Resp. Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.