21750
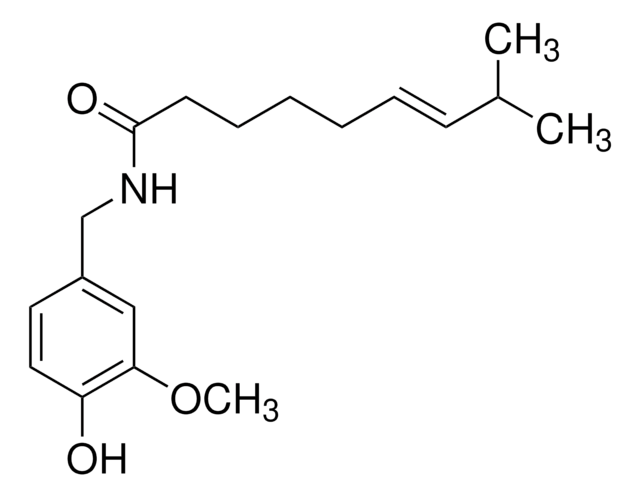
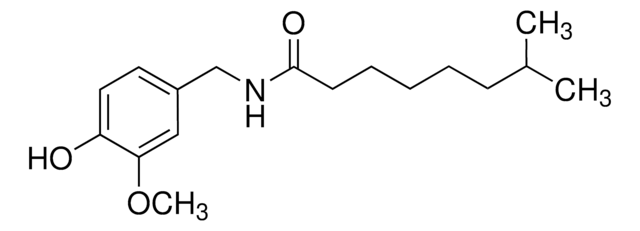
Capsaicin
from Capsicum sp., ≥50% (HPLC)
Sinonimo/i:
8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-trans-6-nonenamide
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
Capsicum sp.
Livello qualitativo
Forma fisica
powder
Concentrazione
≥50% (HPLC)
Impurezze
~35% dihydrocapsaicin
Punto di fusione
62-65 °C (lit.)
62-66 °C
Solubilità
H2O: insoluble
applicazioni
metabolomics
vitamins, nutraceuticals, and natural products
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
COc1cc(CNC(=O)CCCC\C=C\C(C)C)ccc1O
InChI
1S/C18H27NO3/c1-14(2)8-6-4-5-7-9-18(21)19-13-15-10-11-16(20)17(12-15)22-3/h6,8,10-12,14,20H,4-5,7,9,13H2,1-3H3,(H,19,21)/b8-6+
YKPUWZUDDOIDPM-SOFGYWHQSA-N
Informazioni sul gene
human ... CYP1A2(1544) , TRPV1(7442)
rat ... Trpv1(83810) , Trpv4(66026)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 2 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.