759406
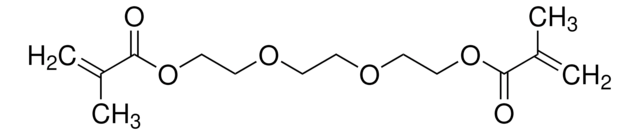
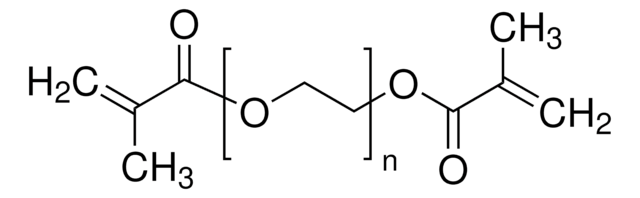
Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate
99%, cross-linking reagent polymerization reactions, 200 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate, contains 200 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor, 99%
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
99%
Stato
liquid
contiene
200 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
Indice di rifrazione
n20/D 1.461 (lit.)
n/D 1.4613
P. ebollizione
170-172 °C/5 mmHg (lit.)
Densità
1.092 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
1.074 g/mL
Architettura del polimero
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
CC(=C)C(=O)OCCOCCOCCOC(=O)C(C)=C
InChI
1S/C14H22O6/c1-11(2)13(15)19-9-7-17-5-6-18-8-10-20-14(16)12(3)4/h1,3,5-10H2,2,4H3
HWSSEYVMGDIFMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- Used as a diluent comonomer in dimethacrylate based dental composites.
- Used as a branching agent in the atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of styrene.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Skin Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
332.6 °F - closed cup
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
167 °C - closed cup
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 759406-1ML | |
| 759406-10ML | 4061837889592 |
| 759406-50ML | 4061837889608 |
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.