RAB0603
Human ALB / Serum albumin ELISA Kit
Sinônimo(s):
Serum Albumin
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
41116158
NACRES:
NA.32
Produtos recomendados
reatividade de espécies
human
embalagem
kit of 96 wells (12 strips x 8 wells)
técnica(s)
ELISA: suitable
entrada
sample type serum
sample type cell culture supernatant(s)
sample type plasma
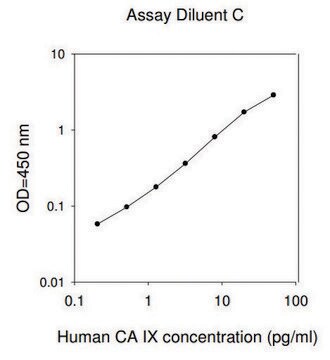
assay range
inter-assay cv: <12%
intra-assay cv: <10%
sensitivity: 6 ng/mL
standard curve range: 4.915-1200 ng/mL
método de detecção
colorimetric
Condições de expedição
wet ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
Informações sobre genes
human ... ALB(213)
Descrição geral
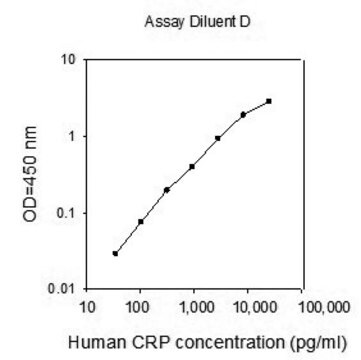
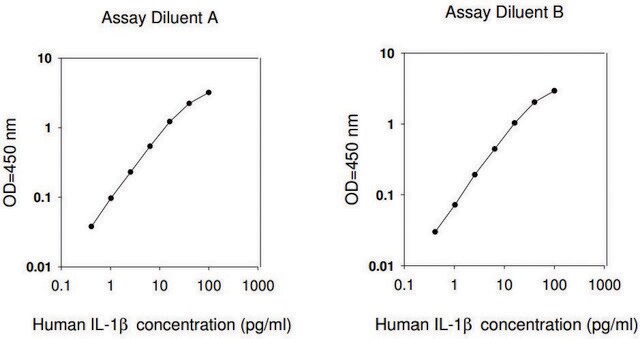
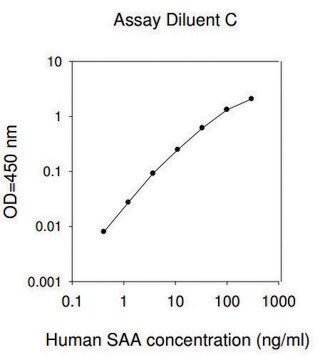
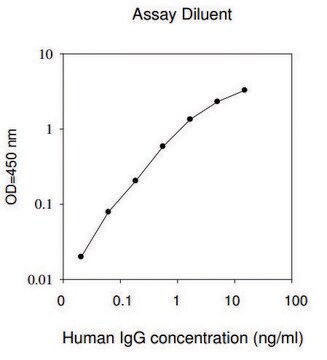
The ALB ELISA kit provides for the quantitative measurement of Albumin in Cell Culture Supernatants, Plasma and Serum.
This ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of a target protein in biological samples, such as serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants, urine and/or cell and tissue lysates.
Aplicação
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Please refer to the attached General ELISA KIT Procedure (sandwich, competitive & Indirect ELISA)
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Human serum albumin (HSA) is a single, non-glycosylated chain that binds to various endogenous and exogenous ligands. It functions as a plasma transporter molecule and primarily binds to non-esterified long-chain fatty acids. Albumin also binds to and transports various metabolites, such as bilirubin, steroid hormones, thyroxin, tryptophan, certain vitamins and metal ions within the body. It also has the ability to bind to several drugs and affects their pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. HSA functions as a nitric oxide-carrier and also influences the antioxidant capacity of human serum. In cases of acute hemolysis, HSA binds to heme in the blood stream and transports to hemopexin, where in it is reabsorbed by parenchymal liver cells.
Outras notas
A sample Certificate of Analysis is available for this product.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Please type the word sample in the text box provided for lot number.
Palavra indicadora
Warning
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Met. Corr. 1
Código de classe de armazenamento
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Chen Zhang et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 12707-12707 (2017-10-07)
Liver disease is a serious problem affecting millions of people with continually increasing prevalence. Stem cell therapy has become a promising treatment for liver dysfunction. We previously reported on human minor salivary gland mesenchymal stem cells (hMSGMSCs), which are highly
Na Du et al.
Renal failure, 39(1), 229-235 (2016-11-24)
DMP-1 supplement has a satisfactory effect on diabetic kidney disease in patients with whether T1DM or T2DM. Oxidative stress and TGF-β signal pathway activation are essential in the pathogenesis of DKD. We aim to investigate the effect of DMP-1 on
A Francesca Setiadi et al.
Journal of neuroimmunology, 332, 147-154 (2019-04-30)
IL-17 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS). Here, we show that blockade of IL-17A, but not IL-17F, attenuated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). We further show that IL-17A levels were elevated in the CSF of relapsing-remitting MS
Cai Zhang et al.
Nature communications, 9(1), 3658-3658 (2018-09-12)
RNA silencing inhibits mRNA translation. While mRNA translation accounts for the majority of cellular energy expenditure, it is unclear if RNA silencing regulates energy homeostasis. Here, we report that hepatic Argonaute 2 (Ago2)-mediated RNA silencing regulates both intrinsic energy production
Qiong Wu et al.
Molecular medicine reports, 16(6), 9473-9479 (2017-11-21)
The development of novel culture systems that mimic the in vivo microenvironment may be beneficial for inducing the differentiation of stem cells and promoting liver function. In the present study, spheroid cultures and decellularized liver scaffolds (DLSs) were utilized to obtain
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica